Purified recombinant human prosaposin forms oligomers that bind procathepsin D and affect its autoactivation
- PMID: 15255780
- PMCID: PMC1133744
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20040175
Purified recombinant human prosaposin forms oligomers that bind procathepsin D and affect its autoactivation
Abstract
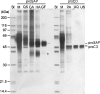
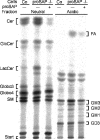
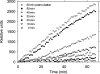
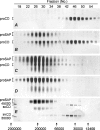
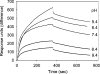
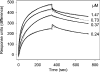
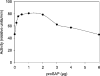
Before delivery to endosomes, portions of proCD (procathepsin D) and proSAP (prosaposin) are assembled into complexes. We demonstrate that such complexes are also present in secretions of cultured cells. To study the formation and properties of the complexes, we purified proCD and proSAP from culture media of Spodoptera frugiperda cells that were infected with baculoviruses bearing the respective cDNAs. The biological activity of proCD was demonstrated by its pH-dependent autoactivation to pseudocathepsin D and that of proSAP was demonstrated by feeding to saposin-deficient cultured cells that corrected the storage of radioactive glycolipids. In gel filtration, proSAP behaved as an oligomer and proCD as a monomer. ProSAP altered the elution of proCD such that the latter was shifted into proSAP-containing fractions. ProSAP did not change the elution of mature cathepsin D. Using surface plasmon resonance and an immobilized biotinylated proCD, binding of proSAP was demonstrated under neutral and weakly acidic conditions. At pH 6.8, specific binding appeared to involve more than one binding site on a proSAP oligomer. The dissociation of the first site was characterized by a K(D1) of 5.8+/-2.9x10(-8) M(-1) (calculated for the monomer). ProSAP stimulated the autoactivation of proCD and also the activity of pseudocathepsin D. Concomitant with the activation, proSAP behaved as a substrate yielding tri- and disaposins and smaller fragments. Our results demonstrate that proSAP forms oligomers that are capable of binding proCD spontaneously and independent of the mammalian type N-glycosylation but not capable of binding mature cathepsin D. In addition to binding proSAP, proCD behaves as an autoactivable and processing enzyme and its binding partner as an activator and substrate.
Figures

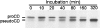

Similar articles
-
The secretion and maturation of prosaposin and procathepsin D are blocked in embryonic neural progenitor cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Aug;1783(8):1480-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2008.01.033. Epub 2008 Feb 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18346466
-
Lysosomal proteolysis of prosaposin, the precursor of saposins (sphingolipid activator proteins): its mechanism and inhibition by ganglioside.Arch Biochem Biophys. 1997 May 1;341(1):17-24. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1997.9958. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1997. PMID: 9143348
-
High yield synthesis and characterization of phosphorylated recombinant human procathepsin D expressed in mammalian cells.Protein Expr Purif. 2006 Jan;45(1):157-67. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2005.07.024. Epub 2005 Aug 19. Protein Expr Purif. 2006. PMID: 16242956
-
Proteolytic activation of human procathepsin D.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;306:289-96. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-6012-4_35. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991. PMID: 1812719 Review.
-
The dilemma: does tissue expression of cathepsin D reflect tumor malignancy? The question: does the assay truly mirror cathepsin D mis-function in the tumor?Cancer Biomark. 2010;7(1):47-64. doi: 10.3233/CBM-2010-0143. Cancer Biomark. 2010. PMID: 21045264 Review.
Cited by
-
Endosomal sorting by Semaphorin 4A in retinal pigment epithelium supports photoreceptor survival.Genes Dev. 2012 Apr 15;26(8):816-29. doi: 10.1101/gad.184481.111. Epub 2012 Mar 30. Genes Dev. 2012. PMID: 22465952 Free PMC article.
-
Sortilin knock-down alters the expression and distribution of cathepsin D and prosaposin and up-regulates the cation-dependent mannose-6-phosphate receptor in rat epididymal cells.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 1;13(1):3461. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-29157-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36859404 Free PMC article.
-
The role of UDP-Glc:glycoprotein glucosyltransferase 1 in the maturation of an obligate substrate prosaposin.J Cell Biol. 2010 May 31;189(5):829-41. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200912105. Epub 2010 May 24. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20498017 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction between progranulin and prosaposin is mediated by granulins and the linker region between saposin B and C.J Neurochem. 2017 Oct;143(2):236-243. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14110. Epub 2017 Aug 4. J Neurochem. 2017. PMID: 28640985 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cathepsin D activity by the FTLD protein progranulin.Acta Neuropathol. 2017 Jul;134(1):151-153. doi: 10.1007/s00401-017-1719-5. Epub 2017 May 10. Acta Neuropathol. 2017. PMID: 28493053 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Qi X., Grabowski G. A. Differential membrane interactions of saposins A and C: implications for the functional specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:27010–27017. - PubMed
-
- Winau F., Schwierzeck V., Hurwitz R., Remmel N., Sieling P. A., Modlin R. L., Porcelli S. A., Brinkmann V., Sugita M., Sandhoff K., et al. Saposin C is required for lipid presentation by human CD1b. Nature Immunol. 2004;5:169–174. - PubMed
-
- Hazkani-Covo E., Altman N., Horowitz M., Graur D. The evolutionary history of prosaposin: two successive tandem-duplication events gave rise to the four saposin domains in vertebrates. J. Mol. Evol. 2002;54:30–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

