Robustness of chlorzoxazone as an in vivo measure of cytochrome P450 2E1 activity
- PMID: 15255802
- PMCID: PMC1884585
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2004.02132.x
Robustness of chlorzoxazone as an in vivo measure of cytochrome P450 2E1 activity
Abstract
Aims: Chlorzoxazone is metabolized by cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1) to a single oxidized metabolite, 6-hydroxychlorzoxazone. The aim of the study was to test the robustness of chlorzoxazone as an in vivo probe of CYP2E1 activity in humans, with emphasis on investigating short-term and long-term intra-individual variabilities and effects of different doses of the drug. In addition, the influences of body build, drug metabolizing enzyme genotype, blood sampling time, and moderate recent ethanol intake were investigated.
Methods: The 6-hydroxychlorzoxazone:chlorzoxazone (metabolic) ratio in plasma was measured at 2 h in 28 male and nine female volunteers following a single oral dose of 500 mg chlorzoxazone. Similarly, the metabolic ratios at 4 h and 6 h were measured in 20 of the males. The metabolic ratio at 2 h was also determined 1.5 and 2.5 years later in 13 and seven males, respectively, and weekly for 3 weeks in seven males, after a dose of 500 mg, once at higher (750 mg) and lower (250 mg) doses, and once (500 mg) following moderate ethanol intake (0.5 g kg(-1) body weight) the preceding evening. Genotypes were determined for CYP2E1 as well as for N-acetyltransferase 2 and glutathione transferase M1.
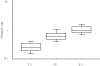
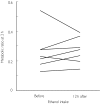
Results: Excluding an outlier (ratio = 1.6) the metabolic ratio at 2 h ranged from 0.12 to 0.61 (n = 36). A positive correlation with body weight (r = 0.61, P < 0.001) suggested dose-dependent metabolism of chlorzoxazone. The metabolic ratio decreased with increasing chlorzoxazone dose (P = 0.01), again suggesting dose-dependent metabolism. Long-term (yearly intervals) and short-term (weekly intervals) intra- and interindividual variabilities in metabolic ratio were similar (30% and 63%vs 28% and 54%, respectively). Both inter- and intra-individual variabilities tended to decrease with increasing dose of chlorzoxazone. There was no significant influence of moderate ethanol intake the preceding evening, or of CYP2E1 genotype on the metabolic ratio.
Conclusions: The relatively low intra-individual variability in the metabolism of chlorzoxazone suggests that a single-sample procedure may suffice to assess CYP2E1 activity in vivo. However, chlorzoxazone metabolism is dose-dependent at commonly used doses and it is therefore advisable to adjust the dose for body weight. Moderate intake of ethanol the preceding evening did not significantly affect the chlorzoxazone metabolic ratio.
Figures

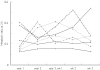
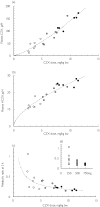
 ), 750 mg (•), curve fit (
), 750 mg (•), curve fit ( )
)Similar articles
-
Impaired 6-hydroxychlorzoxazone elimination in patients with kidney disease: Implication for cytochrome P450 2E1 pharmacogenetic studies.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2003 Dec;74(6):555-68. doi: 10.1016/j.clpt.2003.09.003. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2003. PMID: 14663458 Clinical Trial.
-
Phenotyping of cytochrome P450 2E1 in vitro and in vivo.Curr Drug Metab. 2007 Jun;8(5):493-8. doi: 10.2174/138920007780866843. Curr Drug Metab. 2007. PMID: 17584020 Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of alcohol and diallyl sulphide on CYP2E1 activity in humans: a phenotyping study using chlorzoxazone.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2001 Jul;20(7):321-7. doi: 10.1191/096032701680350587. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2001. PMID: 11530830
-
Cytochrome P450 2E1: its clinical and toxicological role.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2000 Jun;25(3):165-75. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2710.2000.00282.x. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2000. PMID: 10886461 Review.
-
Cytochrome CYP2E1 phenotyping and genotyping in the evaluation of health risks from exposure to polluted environments.Toxicol Lett. 2001 Oct 15;124(1-3):71-81. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4274(00)00287-3. Toxicol Lett. 2001. PMID: 11684359 Review.
Cited by
-
Obesity-induced CYP2E1 activity in children.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Feb;85(2):458-459. doi: 10.1111/bcp.13813. Epub 2018 Dec 9. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30537026 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Ataxic Symptoms in Huntington's Disease Transgenic Mouse Model Are Alleviated by Chlorzoxazone.Front Neurosci. 2020 Apr 3;14:279. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00279. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32317916 Free PMC article.
-
A chlorzoxazone-folic acid combination improves cognitive affective decline in SCA2-58Q mice.Sci Rep. 2023 Aug 3;13(1):12588. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39331-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37537226 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of 2-piperidone as a biomarker of CYP2E1 activity through metabolomic phenotyping.Toxicol Sci. 2013 Sep;135(1):37-47. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kft143. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Toxicol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23811823 Free PMC article.
-
Non randomized study on the potential of nitisinone to inhibit cytochrome P450 2C9, 2D6, 2E1 and the organic anion transporters OAT1 and OAT3 in healthy volunteers.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2019 Mar;75(3):313-320. doi: 10.1007/s00228-018-2581-7. Epub 2018 Nov 15. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30443705 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Wrighton SA, Stevens JC. The human hepatic cytochromes P450 involved in drug metabolism. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1992;22:1–21. - PubMed
-
- Raucy JL. Risk assessment:. toxicity from chemical exposure resulting from enhanced expression of CYP2E1. Toxicology. 1995;105:217–24. - PubMed
-
- Kim H, Wang RS, Elovaara E, et al. Cytochrome P450 isozymes responsible for the metabolism of toluene and styrene in human liver microsomes. Xenobiotica. 1997;27:657–65. - PubMed
-
- Lieber CS. Cytochrome P-4502E1: Its physiological and pathological role. Physiol Rev. 1997;77:517–44. - PubMed
-
- Yoo JS, Guengerich FP, Yang CS. Metabolism of N-nitrosodialkylamines by human liver microsomes. Cancer Res. 1988;48:1499–504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

