Muscleblind proteins regulate alternative splicing
- PMID: 15257297
- PMCID: PMC514918
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600300
Muscleblind proteins regulate alternative splicing
Abstract
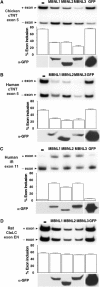
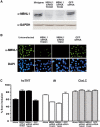
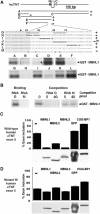
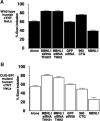
Although the muscleblind (MBNL) protein family has been implicated in myotonic dystrophy (DM), a specific function for these proteins has not been reported. A key feature of the RNA-mediated pathogenesis model for DM is the disrupted splicing of specific pre-mRNA targets. Here we demonstrate that MBNL proteins regulate alternative splicing of two pre-mRNAs that are misregulated in DM, cardiac troponin T (cTNT) and insulin receptor (IR). Alternative cTNT and IR exons are also regulated by CELF proteins, which were previously implicated in DM pathogenesis. MBNL proteins promote opposite splicing patterns for cTNT and IR alternative exons, both of which are antagonized by CELF proteins. CELF- and MBNL-binding sites are distinct and regulation by MBNL does not require the CELF-binding site. The results are consistent with a mechanism for DM pathogenesis in which expanded repeats cause a loss of MBNL and/or gain of CELF activities, leading to misregulation of alternative splicing of specific pre-mRNA targets.
Figures

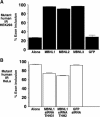
References
-
- Artero R, Prokop A, Paricio N, Begemann G, Pueyo I, Mlodzik M, Perez-Alonso M, Baylies MK (1998) The muscleblind gene participates in the organization of Z-bands and epidermal attachments of Drosophila muscles and is regulated by Dmef2. Dev Biol 195: 131–143 - PubMed
-
- Begemann G, Paricio N, Artero R, Kiss I, Perez-Alonso M, Mlodzik M (1997) Muscleblind, a gene required for photoreceptor differentiation in Drosophila, encodes novel nuclear Cys3His-type zinc-finger-containing proteins. Development 124: 4321–4331 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

