Penetrating keratoplasty: indications over a 10 year period
- PMID: 15258012
- PMCID: PMC1772260
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.2003.031948
Penetrating keratoplasty: indications over a 10 year period
Abstract
Aims: To determine the indications for penetrating keratoplasty (PK) at the Corneoplastic Unit and Eye Bank, UK, a tertiary referral centre, over a 10 year period.
Methods: Records of all patients who underwent PK at our institution between 1990 and 1999 were reviewed retrospectively. Of the 1096 procedures performed in this period, 784 records were available for evaluation (72%).
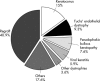
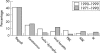
Results: Regrafting was the most common indication, accounting for 40.9% of all cases. Keratoconus was the second most common indication (15%), followed by Fuchs' endothelial dystrophy (9.3%), pseudophakic bullous keratopathy (7.6%), and viral keratitis (5.9%), which included both herpes simplex and herpes zoster and showed a statistically significant decreasing trend using regression analysis (p<0.005). Among the regraft subgroup, viral keratitis accounted for 21.2% as the underlying primary diagnosis. The most common cause for graft failure in the regraft subgroup was endothelial failure (41.8%).
Conclusion: Regrafting is the leading indication for PK; viral disease-although declining-is the leading primary diagnosis.
Figures

References
-
- Smith RE, McDonald HR, Nesburn AB, et al. Penetrating keratoplasty, Changing indications, 1947 to 1978. Arch Ophthalmol 1980;98:1226–9. - PubMed
-
- Lemp MA. Indications for penetrating keratoplasty. Med Ann DC 1972;41:346–50. - PubMed
-
- Arentsen JJ, Morgan B, Green WR. Changing indications for keratoplasty. Am J Ophthalmol 1976;81:313–18. - PubMed
-
- Sharif KW, Casey TA. Changing indications for penetrating keratoplasty, 1971–1990. Eye 1993;7:485–8. - PubMed
-
- Morris RJ, Bates AK. Changing indications for keratoplasty. Eye 1989;3:455–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
