The oxylipin signal jasmonic acid is activated by an enzyme that conjugates it to isoleucine in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 15258265
- PMCID: PMC519202
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.104.023549
The oxylipin signal jasmonic acid is activated by an enzyme that conjugates it to isoleucine in Arabidopsis
Abstract
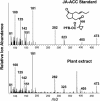
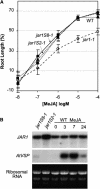
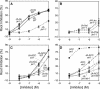
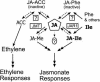
Despite its importance in a variety of plant defense responses, our understanding of how jasmonic acid (JA) functions at the biochemical level is limited. Several amino acid conjugates of JA were tested for their ability to complement the JA-insensitive Arabidopsis thaliana mutant jar1-1. Unlike free JA, JA-Ile inhibited root growth in jar1-1 to the same extent as in the wild type, whereas JA-Val, JA-Leu, and JA-Phe were ineffective inhibitors in both genotypes. Thin-layer chromatography and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) analysis of products produced in vitro by recombinant JAR1 demonstrated that this enzyme forms JA-amido conjugates with several amino acids, including JA-Ile. JA-Val, -Leu, -Ile, and -Phe were each quantified in Arabidopsis seedlings by GC-MS. JA-Ile was found at 29.6 pmole g(-1) fresh weight (FW) in the wild type but was more than sevenfold lower in two jar1 alleles. JA-Leu, -Val, and -Phe were present at only low levels in both genotypes. Expression of wild-type JAR1 in transgenic jar1-1 plants restored sensitivity to JA and elevated JA-Ile to the same level as in the wild type. The ethylene precursor 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) conjugated to JA was also found in plant tissue at 18.4 pmole g(-1) FW. JA-ACC was determined not be an effective jasmonate root inhibitor, and surprisingly, was twofold higher in the mutants than in the wild type. This suggests that another JA-conjugating enzyme(s) is present in Arabidopsis. Synthesis of JA-ACC might provide a mechanism to coregulate the availability of JA and ACC for conversion to the active hormones JA-Ile and ethylene, respectively. We conclude that JAR1 is a JA-amino synthetase that is required to activate JA for optimal signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant hormone activation by conjugation to amino acids and the enzymes involved in their formation were previously unknown.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The role of JAR1 in Jasmonoyl-L: -isoleucine production during Arabidopsis wound response.Planta. 2008 May;227(6):1221-32. doi: 10.1007/s00425-008-0694-4. Epub 2008 Feb 5. Planta. 2008. PMID: 18247047
-
Cytochromes P450 CYP94C1 and CYP94B3 catalyze two successive oxidation steps of plant hormone Jasmonoyl-isoleucine for catabolic turnover.J Biol Chem. 2012 Feb 24;287(9):6296-306. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.316364. Epub 2012 Jan 3. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22215670 Free PMC article.
-
AtGH3.10 is another jasmonic acid-amido synthetase in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant J. 2022 May;110(4):1082-1096. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15724. Epub 2022 Mar 22. Plant J. 2022. PMID: 35247019
-
Chemical and genetic exploration of jasmonate biosynthesis and signaling paths.Planta. 2012 Nov;236(5):1351-66. doi: 10.1007/s00425-012-1705-z. Epub 2012 Jul 28. Planta. 2012. PMID: 23011567 Review.
-
Recent advances in the chemistry and biology of plant oxylipin hormones.Nat Prod Rep. 2025 Jul 16;42(7):1175-1194. doi: 10.1039/d5np00006h. Nat Prod Rep. 2025. PMID: 40275837 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of a novel jasmonate-responsive element in the AtJMT promoter and its binding protein for AtJMT repression.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55482. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055482. Epub 2013 Feb 5. PLoS One. 2013. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2020 Nov 3;15(11):e0242041. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242041. PMID: 23393583 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Co-Transcriptomic Analysis of the Maize-Western Corn Rootworm Interaction.Plants (Basel). 2022 Sep 7;11(18):2335. doi: 10.3390/plants11182335. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145736 Free PMC article.
-
The Ubiquitin System and Jasmonate Signaling.Plants (Basel). 2016 Jan 9;5(1):6. doi: 10.3390/plants5010006. Plants (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27135226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endogenous Bioactive Jasmonate Is Composed of a Set of (+)-7-iso-JA-Amino Acid Conjugates.Plant Physiol. 2016 Dec;172(4):2154-2164. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00906. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27756820 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical genetic screening identifies nalacin as an inhibitor of GH3 amido synthetase for auxin conjugation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Dec 6;119(49):e2209256119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2209256119. Epub 2022 Dec 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36454752 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bleecker, A.B., Estelle, M.A., Somerville, C., and Kende, H. (1988). Insensitivity to ethylene is conferred by a dominant mutation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 241, 1086–1089. - PubMed
-
- Clough, S.J., and Bent, A.F. (1998). Floral dip: A simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 16, 735–743. - PubMed
-
- Conconi, A., Smerdon, M.J., Howe, G.A., and Ryan, C.A. (1996). The octadecanoid signaling pathway in plants mediates a response to ultraviolet radiation. Nature 383, 826–829. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

