Hepatitis B virus X gene induces human telomerase reverse transcriptase mRNA expression in cultured normal human cholangiocytes
- PMID: 15259077
- PMCID: PMC4724980
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i15.2259
Hepatitis B virus X gene induces human telomerase reverse transcriptase mRNA expression in cultured normal human cholangiocytes
Abstract
Aim: To study the transcriptional regulation of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) mRNA in normal human cholangiocytes (HBECs) after hepatitis B virus X (HBx) gene transfection and to elucidate the possible mechanism of HBV infection underlying cholangiocarcinoma.
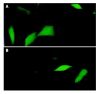
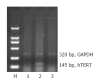
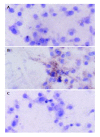
Methods: HBECs were cultured in vitro and co-transfected with a eukaryotic expression vector containing the HBx coding region and a cloning vector containing coding sequences of enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) using lipid-mediated gene transfer. The transfection efficiency was determined by the expression of EGFP. The expressions of hTERT mRNA and HBx protein in HBECs were detected by RT-PCR and immunocytochemical stain, respectively.
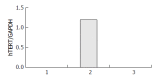
Results: The transfection efficiencies were about 15% for both HBx gene expression plasmid and empty vector. No hTERT mRNA was expressed in HBECs when transfected with OPTI-MEM medium and empty vector, but a dramatic increase was observed for hTERT mRNA expression in HBECs when transfected with HBx expression vector. HBx protein was only expressed in HBECs when transfected with HBx expression vector.
Conclusion: HBx transfection can activate the transcriptional expression of hTERT mRNA. Cis-activation of hTERT mRNA by HBx gene is the primary mechanism underlying the proliferation, differentiation and tumorigenesis of biliary epithelia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Upregulation of human telomerase reverse transcriptase mRNA expression by in vitro transfection of hepatitis B virus X gene into human hepatocarcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma cells.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Sep 28;11(36):5627-32. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i36.5627. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 16237755 Free PMC article.
-
[The effect of hepatitis B virus X gene transfection on expression of human telomerase reverse transcriptase mRNA in human bile duct carcinoma cell lines].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2004 Oct 22;42(20):1254-7. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15598376 Chinese.
-
Effects of hepatitis B virus X protein on human telomerase reverse transcriptase expression and activity in hepatoma cells.J Lab Clin Med. 2005 Feb;145(2):98-104. doi: 10.1016/j.lab.2004.11.018. J Lab Clin Med. 2005. PMID: 15746653
-
Hepatitis B virus X protein upregulates transcriptional activation of human telomerase reverse transcriptase.Virus Genes. 2010 Apr;40(2):174-82. doi: 10.1007/s11262-009-0441-3. Epub 2010 Jan 28. Virus Genes. 2010. PMID: 20107884
-
Effect of plasmid-mediated RNA interference targeting telomerase reverse transcriptase on lung cancer cells.Oncol Rep. 2011 Dec;26(6):1487-95. doi: 10.3892/or.2011.1455. Epub 2011 Sep 12. Oncol Rep. 2011. PMID: 21922145
Cited by
-
Identification of key genes in hepatitis B associated hepatocellular carcinoma based on WGCNA.Infect Agent Cancer. 2021 Mar 16;16(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s13027-021-00357-4. Infect Agent Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33726794 Free PMC article.
-
Cause-specific telomere factors deregulation in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Sep 11;32(1):64. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-32-64. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24020493 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a possible role of hepatitis B virus.J Viral Hepat. 2010 Oct;17(10):742-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2009.01243.x. J Viral Hepat. 2010. PMID: 20002305 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Interplay of Apoptosis and Autophagy.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 13;11(4):1166. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041166. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37189787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum-reduced media impacts on cell viability and protein expression in human lung epithelial cells.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun;234(6):7718-7724. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27890. Epub 2018 Dec 4. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30515823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aragona M, Maisano R, Panetta S, Giudice A, Morelli M, La Torre I, La Torre F. Telomere length maintenance in aging and carcinogenesis. Int J Oncol. 2000;17:981–989. - PubMed
-
- Kim NW, Piatyszek MA, Prowse KR, Harley CB, West MD, Ho PL, Coviello GM, Wright WE, Weinrich SL, Shay JW. Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer. Science. 1994;266:2011–2015. - PubMed
-
- Dhaene K, Van Marck E, Parwaresch R. Telomeres, telomerase and cancer: an up-date. Virchows Arch. 2000;437:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Poole JC, Andrews LG, Tollefsbol TO. Activity, function, and gene regulation of the catalytic subunit of telomerase (hTERT) Gene. 2001;269:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Horikawa I, Barrett JC. cis-Activation of the human telomerase gene (hTERT) by the hepatitis B virus genome. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93:1171–1173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

