Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: current understanding of the pathogenesis and the status of treatment
- PMID: 15262886
- PMCID: PMC450366
- DOI: 10.1503/cmaj.1030055
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: current understanding of the pathogenesis and the status of treatment
Abstract
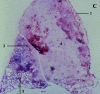
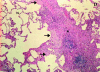
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive and lethal pulmonary fibrotic lung disease. The diagnostic histological changes are called usual interstitial pneumonia and are characterized by histological temporal heterogeneity, whereby normal lung tissue is interspersed with interstitial fibrosis, honeycomb cysts and fibroblast foci. Pulmonary functions show restricted volumes and capacities, preserved flows and evidence of decreased gas exchange. High-resolution computed axial tomography demonstrates evidence of fibrosis and lung remodelling such as honeycomb cysts and traction bronchiectasis. There is no known effective treatment for IPF, but lung transplantation improves survival.
Figures





References
-
- Katzenstein AL, Myers JL. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia and the other idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: classification and diagnostic criteria. Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1-3. - PubMed
-
- Katzenstein AL, Zisman DA, Litzky LA, Nyuyen BT, Kotloff RM. Usual interstitial pneumonia: histologic study of biopsy and explant specimens. Am J Surg Pathol 2002;26:1567-77. - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and treatment. International consensus statement. Am J Respir Crit CareMed 2000; 161: 646-64. - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society. ATS/ERS international consensus classification of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002; 165: 277-304. - PubMed
-
- Epler GR, Colby TV, McCloud TC, Carrington CB, Gaensler EA. Bronchiolitios obliterans organizing pneumonia. N Engl J Med 1985;312:152-8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
