Adaptive point mutation and adaptive amplification pathways in the Escherichia coli Lac system: stress responses producing genetic change
- PMID: 15262914
- PMCID: PMC451650
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.15.4838-4843.2004
Adaptive point mutation and adaptive amplification pathways in the Escherichia coli Lac system: stress responses producing genetic change
Figures
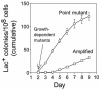
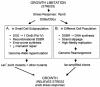
Comment in
-
Rebuttal: adaptive point mutation (Rosenberg and Hastings).J Bacteriol. 2004 Aug;186(15):4844. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.15.4844.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15262915 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Rebuttal: adaptive point mutation (Rosenberg and Hastings).J Bacteriol. 2004 Aug;186(15):4845. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.15.4845.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15262916 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Andersson, D. I., E. S. Slechta, and J. R. Roth. 1998. Evidence that gene amplification underlies adaptive mutability of the bacterial lac operon. Science 282:1133-1135. - PubMed
-
- Bjedov, I., O. Tenaillon, B. Gérard, V. Souza, E. Denamur, M. Radman, F. Taddei, and I. Matic. 2003. Stress-induced mutagenesis in bacteria. Science 300:1404-1409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

