Biochemical study of multiple CheY response regulators of the chemotactic pathway of Rhodobacter sphaeroides
- PMID: 15262956
- PMCID: PMC451638
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.15.5172-5177.2004
Biochemical study of multiple CheY response regulators of the chemotactic pathway of Rhodobacter sphaeroides
Abstract
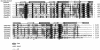
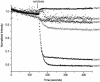
The six copies of the response regulator CheY from Rhodobacter sphaeroides bind to the switch protein FliM. Phosphorylation by acetyl phosphate (AcP) was detected by tryptophan fluorescence quenching in three of the four CheYs that contain this residue. Autophosphorylation with Ac(32)P was observed in five CheY proteins. We also show that all of the cheY genes are expressed simultaneously; therefore, in vivo all of the CheY proteins could bind to FliM to control the chemotactic response. Consequently, we hypothesize that in this complex chemotactic system, the binding of some CheY proteins to FliM, does not necessarily imply switching of the flagellar motor.
Figures

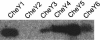

References
-
- Aizawa, S. I., I. B. Zhulin, L. Marquez-Magaña, and G. W. Ordal. 2002. Chemotaxis and motility, p. 437-452. In A. L. Sonenshein, R. Losick, and J. A. Hoch (ed.), Bacillus subtilis and its closest relatives: from genes to cells. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C.
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1987. Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, N.Y.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

