Cathepsin K: a cysteine protease with unique kinin-degrading properties
- PMID: 15265002
- PMCID: PMC1133743
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20040864
Cathepsin K: a cysteine protease with unique kinin-degrading properties
Abstract
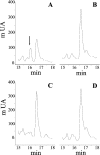
Taking into account a previous report of an unidentified enzyme from macrophages acting as a kininase, the ability of cysteine proteases to degrade kinins has been investigated. Wild-type fibroblast lysates from mice, by contrast with cathepsin K-deficient lysates, hydrolysed BK (bradykinin), and released two metabolites, BK-(1-4) and BK-(5-9). Cathepsin K, but not cathepsins B, H, L and S, cleaved kinins at the Gly4-Phe5 bond and the bradykinin-mimicking substrate Abz (o-aminobenzoic acid)-RPPGFSPFR-3-NO2-Tyr (3-nitrotyrosine) more efficiently (pH 6.0: kcat/K(m)=12500 mM(-1) x s(-1); pH 7.4: kcat/K(m)=6930 mM(-1) x s(-1)) than angiotensin-converting enzyme hydrolysed BK. Conversely Abz-RPPGFSPFR-3-NO2-Tyr was not cleaved by the Y67L (Tyr67-->Leu)/L205A (Leu205-->Ala) cathepsin K mutant, indicating that kinin degradation mostly depends on the S2 substrate specificity. Kininase activity was further evaluated on bronchial smooth muscles. BK, but not its metabolites BK(1-4) and BK(5-9), induced a dose-dependent contraction, which was abolished by Hoe140, a B2-type receptor antagonist. Cathepsin K impaired BK-dependent contraction of normal and chronic hypoxic rats, whereas cathepsins B and L did not. Taking together vasoactive properties of kinins and the potency of cathepsin K to modulate BK-dependent contraction of smooth muscles, the present data support the notion that cathepsin K may act as a kininase, a unique property among mammalian cysteine proteases.
Figures
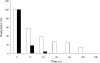


Similar articles
-
Probing cathepsin K activity with a selective substrate spanning its active site.Biochem J. 2003 Oct 15;375(Pt 2):307-12. doi: 10.1042/BJ20030468. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12837132 Free PMC article.
-
Kininogen-derived peptides for investigating the putative vasoactive properties of human cathepsins K and L.Eur J Biochem. 2003 Jan;270(1):171-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2003.03382.x. Eur J Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12492488
-
Modulation of hypotensive effects of kinins by cathepsin K.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2007 Mar 1;459(1):129-36. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2006.10.033. Epub 2006 Nov 9. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2007. PMID: 17181996
-
The consequences of lysosomotropism on the design of selective cathepsin K inhibitors.Chembiochem. 2006 Oct;7(10):1525-35. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200600149. Chembiochem. 2006. PMID: 16921579 Review.
-
The role of cathepsins in osteoimmunology.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2013;23(1):11-26. doi: 10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.2013005929. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2013. PMID: 23557334 Review.
Cited by
-
Future of anticathepsin K drugs: dual therapy for skeletal disease and atherosclerosis?Future Med Chem. 2009 Apr;1(1):21-34. doi: 10.4155/fmc.09.4. Future Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 20126511 Free PMC article.
-
Novel pycnodysostosis mouse model uncovers cathepsin K function as a potential regulator of osteoclast apoptosis and senescence.Hum Mol Genet. 2007 Feb 15;16(4):410-23. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl474. Epub 2007 Jan 8. Hum Mol Genet. 2007. PMID: 17210673 Free PMC article.
-
Eating the brain - A multidisciplinary study provides new insights into the mechanisms underlying the cytopathogenicity of Naegleria fowleri.PLoS Pathog. 2025 Mar 17;21(3):e1012995. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012995. eCollection 2025 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40096149 Free PMC article.
-
Cathepsin K inhibitors for osteoporosis and potential off-target effects.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2009 May;18(5):585-600. doi: 10.1517/13543780902832661. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19388876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cysteine Cathepsins as Therapeutic Targets in Immune Regulation and Immune Disorders.Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 7;11(2):476. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020476. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36831012 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Heitsch H. Bradykinin B2 receptor as a potential therapeutic target. Drug News Perspect. 2000;13:213–225. - PubMed
-
- Wright A. L. Epidemiology of asthma and recurrent wheeze in childhood. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2002;22:33–44. - PubMed
-
- Coulson F. R., Fryer A. D. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and airway diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003;98:59–69. - PubMed
-
- Bhoola K. D., Figueroa C. D., Worthy K. Bioregulation of kinins: kallikreins, kininogens, and kininases. Pharmacol. Rev. 1992;44:1–80. - PubMed
-
- Scuri M., Forteza R., Lauredo I., Sabater J. R., Botvinnikova Y., Allegra L., Abraham W. M. Inhaled porcine pancreatic elastase causes bronchoconstriction via a bradykinin-mediated mechanism. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000;89:1397–1402. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

