Triazine dyes are agonists of the NAADP receptor
- PMID: 15265807
- PMCID: PMC1575193
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705886
Triazine dyes are agonists of the NAADP receptor
Abstract
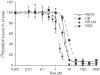
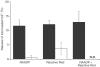
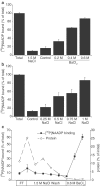
NAADP has been shown to be a potent calcium-releasing second messenger in a wide variety of cell types to date. However, research has been hampered by a lack of pharmacological agents, with which to investigate NAADP-induced calcium release, and by the molecular identity of its cellular target protein being unknown. In the present paper, the sea urchin egg model was used to investigate whether triazine dyes, which can act as nucleotide mimetics, can bind to the NAADP receptor, induce Ca(2+) release and be used for affinity chromatography of the receptor. Indeed, all the triazine dyes tested (Reactive Red 120 (RR120), Reactive Green 19 (RG19), Reactive Green 5 (RG5), Cibacron Blue 3GA and Reactive Yellow 86) displayed micromolar affinities, except for Reactive Orange 14. Furthermore, unlike NAADP, RR120, RG19 and RG5 did not bind in an irreversible manner. The compound that displayed the highest affinity, RR120, was tested in a (45)Ca(2+) efflux assay. This compound released Ca(2+) via the NAADP receptor, as shown by the ability of subthreshold NAADP concentrations to inhibit this release. Furthermore, heparin and ruthenium red were unable to block RR120-induced Ca(2+) release. We have also shown that RG5 and RG19, immobilised on resins, retain the ability to bind to the receptor, and that this interaction can be disrupted by high salt concentrations. As a proof of principle, we have shown that this can be used to partially purify the NAADP receptor by at least 75-fold. In conclusion, triazine dyes interact with the NAADP receptor, and this could be exploited in future to create a new generation of pharmacological tools to investigate this messenger and, in combination with other techniques, to purify the receptor.
Figures
Comment in
-
The NAADP receptor: commentary on Billington et al.Br J Pharmacol. 2004 Aug;142(8):1203-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705888. Epub 2004 Jul 20. Br J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15265809 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- AARHUS R., DICKEY D.M., GRAEFF R.M., GEE K.R., WALSETH T.F., LEE H.C. Activation and inactivation of Ca2+ release by NAADP+ J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:8513–8516. - PubMed
-
- BAK J., BILLINGTON R.A., GENAZZANI A.A. Effect of luminal and extravesicular Ca2+ on NAADP binding and release properties. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002;295:806–811. - PubMed
-
- BERRIDGE G., DICKINSON G., PARRINGTON J., GALIONE A., PATEL S. Solubilization of receptors for the novel Ca2+-mobilising messenger, nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 2002;277:43717–43723. - PubMed
-
- BILLINGTON R.A., GENAZZANI A.A. Characterization of NAADP+ binding in sea urchin eggs. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000;276:112–116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

