Topical umbilical cord care at birth
- PMID: 15266437
- PMCID: PMC6457922
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001057.pub2
Topical umbilical cord care at birth
Abstract
Background: Umbilical cord infection caused many neonatal deaths before aseptic techniques were used.
Objectives: To assess the effects of topical cord care in preventing cord infection, illness and death.
Search strategy: We searched the Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group trials register (September 2003) and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (The Cochrane Library, Issue 2, 2003). We also contacted experts in the field.
Selection criteria: Randomized and quasi-randomized trials of topical cord care compared with no topical care, and comparisons between different forms of care.
Data collection and analysis: Two reviewers assessed trial quality and extracted data.
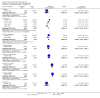
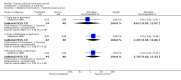
Main results: Twenty-one studies (8959 participants) were included, the majority of which were from high-income countries. No systemic infections or deaths were observed in any of the studies reviewed. No difference was demonstrated between cords treated with antiseptics compared with dry cord care or placebo. There was a trend to reduced colonization with antibiotics compared to topical antiseptics and no treatment. Antiseptics prolonged the time to cord separation. Use of antiseptics was associated with a reduction in maternal concern about the cord.
Reviewers' conclusions: Good trials in low-income settings are warranted. In high-income settings, there is limited research which has not shown an advantage of antibiotics or antiseptics over simply keeping the cord clean. Quality of evidence is low.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures















Update of
-
Topical umbilical cord care at birth.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(2):CD001057. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001057. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(3):CD001057. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001057.pub2. PMID: 10796230 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Arad 1981 {published data only}
Bain 1994 {published data only}
-
- Bain J. Umbilical cord care in pre‐term babies. Nursing Standard 1994;8(15):32‐6. - PubMed
Barrett 1979 {published data only}
-
- Barrett FF, Mason EO, Fleming D. The effect of three cord care regimens on the bacterial colonization of normal newborn infants. Journal of Pediatrics 1979;94:796‐800.
Dore 1998 {published data only}
-
- Dore S, Buchan D, Coulas S, Hamber L, Stewart M, Cowan D, et al. Alcohol versus natural drying for newborn cord care. Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic and Neonatal Nursing 1998;27:621‐7. - PubMed
Gladstone 1988 {published data only}
-
- Gladstone IM, Clapper L, Thorp JW, Wright DI. Randomized study of six umbilical cord care regimens. Clinical Pediatrics 1988;27:127‐9. - PubMed
Golombek 2002 {published data only}
-
- Golombek SG, Brill PE, Salice AL. Randomized trial of alcohol versus triple dye for umbilical cord care. Clinical Pediatrics 2002;41(6):419‐23. - PubMed
Hsu 1999 {published data only}
-
- Hsu CF, Wang CC, Yuh YS, Chen YH, Chu ML. The effectiveness of single and multiple applications of triple dye on umbilical cord separation time. European Journal of Pediatrics 1999;158:144‐6. - PubMed
Janssen 2003 {published data only}
-
- Janssen PA, Selwood BL, Dobson SR, Peacock D, Thiessen PN. To dye or not to dye: a randomized clinical trial of a triple dye/alcohol regime versus dry cord care. Pediatrics 2003;111(1):15‐20. - PubMed
Meberg 1985 {published data only}
-
- Meberg A, Schoyen R. Bacterial colonization and neonatal infections. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica 1985;74:366‐71. - PubMed
Meberg 1990 {published data only}
-
- Meberg A, Schoyen R. Hydrophobic material in routine umbilical cord care and prevention of infections in newborn infants. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1990;22:729‐33. - PubMed
Medves 1997 {published data only}
Mugford 1986 {published data only}
-
- Mugford M, Somchiwong M, Waterhouse I. Treatment of umbilical cords: a randomised trial to assess the effect of treatment methods on the work of midwives. Midwifery 1986;2:177‐86. - PubMed
Panyavudhikrai 2002a {published data only}
-
- Panyavudhikrai S, Danchaivijity S, Vantanasiri C, Trakulsomboon S, Kolatat T, Dhiraputra C, et al. Antiseptics for preventing omphalitis. Journal of Medical Association of Thailand 2002;85(2):229‐33. - PubMed
Panyavudhikrai 2002b {published data only}
-
- Panyavudhikrai S, Danchaivijity S, Vantanasiri C, Trakulsomboon S, Kolatat T, Dhiraputra C, et al. Antiseptics for preventing omphalitis. Journal of Medical Association of Thailand 2002;85(2):229‐33. - PubMed
Perapoch 1993 {published data only}
-
- Perapoch Lopez JP, Abizanda SS, Catala AG, Monforte GP, Caro MC, Perez CB, et al. Colonization of the umbilical cord in normal neonates: comparative assessment of four antiseptic methods applied to the umbilical stump [Colonizacion umbilical en recien nacidos normales. Estudio comparativo de cuatro metodos de antisepsia umbilical]. Anales Espanoles de Pediatria 1993;39(3):195‐8. - PubMed
Pezzati 2002 {published data only}
-
- Pezzati M, Biagioli EC, Martelli E, Gambi B, Biagotti R, Rubaltelli FF. Umbilical cord care: the effect of eight different cord‐care regimens on cord separation time and other outcomes. Biology of the Neonate 2002;81:38‐44. - PubMed
Rosenfeld 1990 {published data only}
-
- Rosenfeld CR, Laptook AR, Jeffery J. Limited effectiveness of triple dye (TD) in prevention of colonization with methacillin‐resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in a special care nursery (SCN). Pediatric Research 1989;25:281A. - PubMed
-
- Rosenfeld CR, Laptook AR, Jeffery J. Limited effectiveness of triple dye in preventing colonization with methicillin‐resistant staphylococcus aureus in a special care nursery. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 1990;9(4):290‐1. - PubMed
Rush 1986 {published data only}
-
- Rush J. Does routine newborn bathing reduce staphylococcus aureus colonization rates? A randomized controlled trial. Birth 1986;13:176‐80. - PubMed
Schuman 1985 {published data only}
-
- Schuman AJ, Oksol BA. The effect of isopropyl alcohol and triple dye on umbilical cord separation time. Military Medicine 1985;150:49‐50. - PubMed
Speck 1980 {published data only}
-
- Speck WT, Driscoll JM, O'Neil J, Rosenkranz HS. Effect of antiseptic cord care on bacterial colonization in the newborn infant. Chemotherapy 1980;26:372‐6. - PubMed
Wald 1977 {published data only}
-
- Wald ER, Snyder MJ, Gutberlet RL. Group B ß‐hemolytic streptococcal colonization. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1977;131(2):178‐80. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Alder 1980 {published data only}
Barclay 1994 {published data only}
-
- Barclay L, Harrington A, Conroy R, Royal R, LaForgia J. A comparative study of neonates’ umbilical cord management. Australian Journal of Advanced Nursing 1994;11:34‐40. - PubMed
Bhakoo 1969 {published data only}
-
- Bhakoo ON, Lall JC, Agarwal KC. Prevention of hospital infections in neonates: an evaluation of no bath regimen. Indian Pediatrics 1969;6(11):697‐700. - PubMed
Birenbaum 1990 {published data only}
-
- Birenbaum HJ, Glorioso L, Rosenberger C, Arshad C, Edwards K. Gowning on a postpartum ward fails to decrease colonization in the newborn infant. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1990;144:1031‐3. - PubMed
Bourke 1990 {published data only}
-
- Bourke E. Cord care: too much or too little. Australian Journal of Advanced Nursing 1990;7(2):19‐22. - PubMed
Bradshaw 1993 {unpublished data only}
-
- Bradshaw C. An experimental study to compare treatment vs non treatment of the umbilical cord. National Conference on Research in Midwifery, Birmingham; 1993 Sept 14; Birmingham, UK, 1993.
Branchi 1998 {published data only}
-
- Branchi M, Bernardini E, Bordont G, Siani A, Bonora G. Bacterial colonisation and time of detachment of umbilical cord: comparative study between alcohol and salicylic sugar [Colonizzazione batterica e tempo di caduta del moncone ombelicale: confronto fra trattamento con alcool e con zucchero salicilico]. Rivista Italiana di Pediatria 1998;24:994‐1004.
Coyer 1975 {published data only}
-
- Coyer WF. Neonatal skin care and the prevention of staphylococcal aureus (staph) colonization. Pediatric Research 1975;9:339.
Gezon 1964 {published data only}
-
- Gezon HM, Thompson DJ, Rogers KD, Hatch TF, Taylor PM. Hexachlorophene bathing in early infancy. New England Journal of Medicine 1964;270:379‐86. - PubMed
Gluck 1963 {published data only}
-
- Gluck L, Wood HF. Staphylococcal colonisation in newborn infants with and without antiseptic skin care. New England Journal of Medicine 1963;268:1265‐8. - PubMed
Henningsson 1981 {published data only}
-
- Henningsson A, Nystrom B, Tunnell R. Bathing or washing babies after birth?. Lancet 1981;2:1401‐3. - PubMed
Hnatko 1977 {published data only}
Jellard 1957 {published data only}
Kwong 1973 {published data only}
-
- Kwong MS, Loew AD, Anthony FA, Oh W. The effect of hexachlorophene on staphylococcal colonization rates in the newborn infant: a controlled study using a single‐bath method. Journal of Pediatrics 1973;82:982‐6. - PubMed
Olowe 1980 {published data only}
-
- Olowe SA, Ransome‐Kuti O. The risk of jaundice in glucose‐6‐phosphat dehydrogenase deficient babies exposed to menthol. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica 1980;69:341‐5. - PubMed
Oxford 1991 {published data only}
-
- Oxford Midwives Research Group. A study of the relationship between the delivery to cord clamping interval and the time of cord separation. Midwifery 1991;7:167‐76. - PubMed
Pildes 1973 {published data only}
-
- Pildes RS, Ramamurth RS, Vidyasagar D. Effect of triple dye on staphylococcal colonisation in the newborn infant. Journal of Pediatrics 1973;82:987‐90. - PubMed
Pyati 1977 {published data only}
-
- Pyati SP, Ramamurthy RS, Krauss MT, Pildes RS. Absorption of iodine in the neonate following topical use of povidone iodine. Journal of Pediatrics 1977;91(5):825‐8. - PubMed
Smales 1988 {published data only}
-
- Smales O. A comparison of umbilical cord treatment in the control of superficial infection. New Zealand Medical Journal 1988;101:453‐5. - PubMed
Thomas 1979 {published data only}
-
- Thomas WR. The prevention of superficial infection in neonates. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1979;5(2):235‐6. - PubMed
Verber 1993 {published data only}
Watkinson 1992 {published data only}
-
- Watkinson M, Dyas A. Staphylococcus aureus still colonizes the untreated neonatal umbilicus. Journal of Hospital Infection 1992;24:131‐6. - PubMed
Wojciechowska 1989 {published data only}
-
- Wojciechowska L. Trial to assess the effects of different treatments of the umbilical cord in newborn infants. Personal Communication 1989.
References to studies awaiting assessment
Bhalla 1975 {published data only}
-
- Bhalla JN, Nafis N, Robargi P, Singh J. Some observations on separation of the umbilical stump in the newborn. Indian Journal of Paediatrics 1975;42:329‐34. - PubMed
Guinsburg 1991 {unpublished data only}
-
- Guinsburg R, Ikezawa MK, Foglilano RRF, Reichert MCF, Carvalho ES, Cardo DM, et al. Umbilical bacterial colonization (UBC) of normal newborn (NB) infants: effect of four antiseptic regimens. Pediatric Research 1991;29:282A.
Huang 2001 {published data only}
-
- Huang C, Yeh L, Chuang M, Yuh Y. Umbilical separation time delayed by alcohol application. Journal of Perinatal Medicine 2001;29 Suppl 1(Pt 2):648.
Pezzati 2003 {published data only}
-
- Pezzati M, Rossi S, Tronchin M, Dani C, Filippi L, Rubaltelli FF. Umbilical cord care in premature Infants: the effect of two different cord‐care regimens (salicylic sugar powder vs chlorhexidine) on cord separation time and other outcomes. Pediatrics 2003;112(4):e275. - PubMed
Ronchera‐Oms 1994 {published data only}
Speck 1977 {published data only}
-
- Speck WT, Driscoll JM, Polin RA, O'Neill J, Rosenkranz HS. Staphylococcal and streptococcal colonization of the newborn infant. American Journal of Diseases in Childhood 1977;131:1005‐8. - PubMed
-
- Speck WT, Driscoll JM, Polin RA, Rosenkranz HS. Bacterial colonization in the newborn ‐ effect of cord care. Pediatric Research 1976;10:335.
Additional references
Aggett 1981
Bennett 1999
-
- Bennett J, Ma C, Traverso H, Agha SB, Boring J. Neonatal tetanus associated with topical umbilical ghee: covert role of cow dung. International Journal of Epidemiology 1999;28:1172‐5. - PubMed
CHRPSR 1999
-
- Anonymous. Reducing perinatal and neonatal mortality. Child Health Research Project Special Report; 1999 May 10 ‐12; Baltimore, Maryland USA. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University, 1999.
Cullen 1916
-
- Cullen TS. Embryology, anatomy and diseases of the umbilicus. Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 1916.
Elhassani 1984
-
- Elhassani SB. The umbilical cord: care, anomalies, and diseases. Southern Medical Journal 1984;77(6):730‐6. - PubMed
Enkin 2000
-
- Enkin M, Keirse MJNC, Neilson J, Crowther C, Duley L, Hodnett E, et al. Mother and baby. A guide to effective care in pregnancy and childbirth. 3rd Edition. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2000:429‐38.
Forshall 1957
Meegan 2001
-
- Meegan ME, Conroy RM, Ole Lengeny S, Renhault K, Nyangole J. Effect on neonatal tetanus mortality after a culturally‐based health promotion programme. Lancet 2001;358:640‐1. - PubMed
Novack 1988
-
- Novack AH, Mueller B, Ochs H. Umbilical cord separation in the normal newborn. American Journal of Diseases in Childhood 1988;142:220‐3. - PubMed
OudesluysMurphy 1987
-
- Oudesluys‐Murphy AM. The time of separation of the umbilical cord. European Journal of Pediatrics 1987;146(4):387‐9. - PubMed
OudesluysMurphy 1990
-
- Oudeluys‐Murphy AM, Hollander JC. Separation of the umbilical cord ‐ histological findings. Biology of the Neonate 1990;58:54‐6. - PubMed
Sarkany 1967
-
- Sarkany I, Gaylarde CC. Skin flora of the newborn. Lancet 1967;1(7490):589‐90. - PubMed
Thayaparan 1998
-
- Thayaparan B, Nicoll A. Prevention and control of tetanus in childhood. Current Opinion in Pediatrics 1998;10(1):4‐8. - PubMed
WHO 1998a
-
- World Health Organization. Care of the umbilical cord: a review of the evidence. World Health Organization WHO/RHT/MSM/98.4 1998.
WHO 1998b
-
- World Health Organization. Epi information systems: Global summary, September 1998. Geneva: WHO/EPI/GEN/98.10, 1998.
Woodruff 1984
-
- Woodruff AW, Grant J, Bashir EA, Baya EI, Yugusuk AZ, Sumi A. Neonatal tetanus: mode of infection, prevalence, and prevention in southern Sudan. Lancet 1984;1(8373):378‐379. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
CDSR 2004
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

