Echocardiographic assessment and percutaneous closure of multiple atrial septal defects
- PMID: 15268761
- PMCID: PMC497050
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-7120-2-9
Echocardiographic assessment and percutaneous closure of multiple atrial septal defects
Abstract
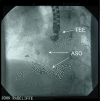
Atrial septal defect closure is now routinely performed using a percutaneous approach under echocardiographic guidance. Centrally located, secundum defects are ideal for device closure but there is considerable morphological variation in size and location of the defects. A small proportion of atrial septal defects may have multiple fenestrations and these are often considered unsuitable for device closure. We report three cases of multiple atrial septal defects successfully closed with two Amplatzer septal occluders.
Figures

References
-
- Omeish A, Hijazi ZM. Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects in children & adults using the Amplatzer Septal Occluder. J Interv Cardiol. 2001;14:37–44. - PubMed
-
- Pedra CA, Fontes-Pedra SR, Esteves CA, Assef J, Fontes VF, Hijazi ZM. Multiple atrial septal defects and patent ductus arteriosus: successful outcome using two Amplatzer septal occluders and Gianturco coils. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn. 1998;45:257–9. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0304(199811)45:3<257::AID-CCD8>3.0.CO;2-U. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Suarez J, Medina A, Pan M, Romero M, Segura J, Pavlovic D, Hernandez E, Delgado A, Caballero E, Siles J, Franco M, Mesa D, Lafuente M. Transcatheter occlusion of complex atrial septal defects. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2000;51:33–41. doi: 10.1002/1522-726X(200009)51:1<33::AID-CCD9>3.0.CO;2-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

