Presentation of vitamin D deficiency
- PMID: 15269083
- PMCID: PMC1720051
- DOI: 10.1136/adc.2003.031385
Presentation of vitamin D deficiency
Abstract
Aims: To describe the various ways in which vitamin D deficiency presents in children in selected districts of London and to identify which factors, if any, determine the mode of presentation.
Methods: Retrospective review of patients presenting to Newham General, Royal London, Great Ormond Street, and King's College Hospitals between 1996 and 2001 with either hypocalcaemia or rickets caused by vitamin D deficiency. Children with plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels <25 nmol/l (10 ng/ml) were considered to have vitamin D deficiency.
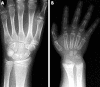
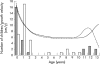
Results: Sixty five children, mostly from Black or Asian ethnic minority groups, were identified, 29 of whom had hypocalcaemic symptoms. Seventeen of these had no radiological evidence of rickets. The remainder (48 children) had radiological evidence of rickets with or without clinical signs. Symptoms and signs reverted to normal in all cases with vitamin D supplementation. All children who presented with symptomatic hypocalcaemia were aged either <3 or >10 years. There was a strong correlation between age at presentation and population growth velocity reference data.
Conclusions: Rickets remains a problem in the UK especially in "at risk" ethnic minority groups. Symptomatic hypocalcaemia is an important, but under-recognised presenting feature. Growth rate is likely to be an important factor in determining the mode of presentation. Unexplained hypocalcaemia should be attributed to vitamin D deficiency in "at risk" ethnic minority groups until proved otherwise.
Figures
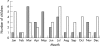
Comment in
-
Maternal vitamin D deficiency, refractory neonatal hypocalcaemia, and nutritional rickets.Arch Dis Child. 2005 Apr;90(4):437-8. doi: 10.1136/adc.2004.065268. Arch Dis Child. 2005. PMID: 15781946 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Nutritional rickets is increasingly diagnosed in children of ethnic origin.Arch Dis Child. 2005 Nov;90(11):1203-4. Arch Dis Child. 2005. PMID: 16243886 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
