Absence of C1q leads to less neuropathology in transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 15269255
- PMCID: PMC6729885
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0901-04.2004
Absence of C1q leads to less neuropathology in transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
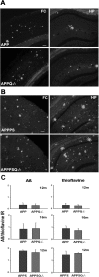
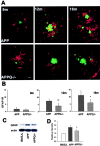
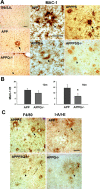
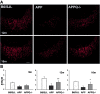
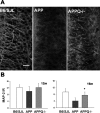
C1q, the recognition component of the classical complement activation pathway, is a multifunctional protein known to be expressed in brain of Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients. To experimentally address the role of C1q in AD, a mouse model lacking C1q (APPQ-/-) was generated by crossing Tg2576 animals (APP) with C1q-deficient mice. The pathology of APPQ-/- was compared with that of APP mice and B6SJL controls at 3-16 months of age by immunohistochemistry and Western blot analysis. At younger ages (3-6 months), when no plaque pathology was present, no significant differences were seen in any of the neuronal or glial markers tested. At older ages (9-16 months), the APP and APPQ-/- mice developed comparable total amyloid and fibrillar beta-amyloid in frontal cortex and hippocampus; however, the level of activated glia surrounding the plaques was significantly lower in the APPQ-/- mice at 12 and 16 months. In addition, although Tg2576 mice showed a progressive decrease in synaptophysin and MAP2 in the CA3 area of hippocampus compared with control B6SJL at 9, 12, and 16 months, the APPQ-/- mice had significantly less of a decrease in these markers at 12 and 16 months. In a second murine model for AD containing transgenes for both APP and mutant presenilin 1 (APP/PS1), a similar reduction of pathology was seen in the APPPS1Q-/- mice. These data suggest that at ages when the fibrillar plaque pathology is present, C1q exerts a detrimental effect on neuronal integrity, most likely through the activation of the classical complement cascade and the enhancement of inflammation.
Figures

References
-
- Afagh A, Cummings BJ, Cribbs DH, Cotman CW, Tenner AJ (1996) Localization and cell association of C1q in Alzheimer's disease brain. Exp Neurol 138: 22-32. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cole GM, Cooper NR, Eikelenboom P, Emmerling M, Fiebich BL, Finch CE, Frautschy S, Griffin WS, Hampel H, Hull M, Landreth G, Lue L, Mrak R, Mackenzie IR, McGeer PL, et al. (2000) Inflammation and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 21: 383-421. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Apelt J, Schliebs R (2001) Beta-amyloid-induced glial expression of both pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in cerebral cortex of aged transgenic Tg2576 mice with Alzheimer plaque pathology. Brain Res 894: 21-30. - PubMed
-
- Ashe KH (2001) Learning and memory in transgenic mice modeling Alzheimer's disease. Learn Mem 8: 301-308. - PubMed
-
- Bartoo GT, Nochlin D, Chang D, Kim Y, Sumi SM (1997) The mean A beta load in the hippocampus correlates with duration and severity of dementia in subgroups of Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 56: 531-540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
