CCAAT displacement protein/cut homolog recruits G9a histone lysine methyltransferase to repress transcription
- PMID: 15269344
- PMCID: PMC509191
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0401343101
CCAAT displacement protein/cut homolog recruits G9a histone lysine methyltransferase to repress transcription
Abstract
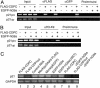
CCAAT displacement protein/cut homolog (CDP/cut) is a highly conserved homeodomain protein that contains three cut repeat sequences. CDP/cut is a transcriptional factor for many diverse cellular and viral genes that are involved in most cellular processes, including differentiation, development, and proliferation. Here, we report that CDP/cut interacts with a histone lysine methyltransferase (HKMT), G9a, in vivo and in vitro. The deletion of the cut repeats within CDP/cut abrogates the interaction with G9a. The transcriptional repressor function of CDP/cut is mediated through HKMT activity of G9a associated with CDP/cut. We show that the recruitment of G9a to the human p21(waf1/cdi1) promoter is contingent on the interaction with CDP/cut, and CDP/cut is directly associated with an increase in the methylation in vivo of Lys-9 in histone H3 within the CDP/cut-regulatory region of the p21(waf1/cdi1) promoter. The endogenous level of p21(waf1/cdi1) expression is repressed through CDP/cut and mediated by HKMT activity of G9a. Furthermore, we report the identification of G9a as a component of CDP/cut complex. G9a colocalizes with CDP/cut in the nucleus. These results indicate that G9a functions as a transcriptional corepressor in association with a CDP/cut complex. These studies now reveal the interaction of G9a with a sequence-specific transcription factor that regulates gene repression through CDP/cut.
Figures

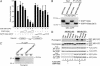


References
-
- Skalnik, D. G., Strauss, E. C. & Orkin, S. H. (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266, 16736–16744. - PubMed
-
- van Wijnen, A. J., Cooper, C., Odgren, P., Aziz, F., De Luca, A., Shakoori, R. A., Giordano, A., Quesenberry, P. J., Lian, J. B., Stein, G. S., et al. (1997) J. Cell. Biochem. 66, 512–523. - PubMed
-
- van Gurp, M. F., Pratap, J., Luong, M., Javed, A., Hoffmann, H., Giordano, A., Stein, J. L., Neufeld, E. J., Lian, J. B., Stein, G. S., et al. (1999) Cancer Res. 59, 5980–5988. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

