Non-selective cationic channels of smooth muscle and the mammalian homologues of Drosophila TRP
- PMID: 15272031
- PMCID: PMC1665181
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.068734
Non-selective cationic channels of smooth muscle and the mammalian homologues of Drosophila TRP
Erratum in
- J Physiol. 2004 Nov 1;560(Pt 3):949
Abstract
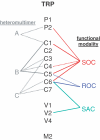
Throughout the body there are smooth muscle cells controlling a myriad of tubes and reservoirs. The cells show enormous diversity and complexity compounded by a plasticity that is critical in physiology and disease. Over the past quarter of a century we have seen that smooth muscle cells contain--as part of a gamut of ion-handling mechanisms--a family of cationic channels with significant permeability to calcium, potassium and sodium. Several of these channels are sensors of calcium store depletion, G-protein-coupled receptor activation, membrane stretch, intracellular Ca2+, pH, phospholipid signals and other factors. Progress in understanding the channels has, however, been hampered by a paucity of specific pharmacological agents and difficulty in identifying the underlying genes. In this review we summarize current knowledge of these smooth muscle cationic channels and evaluate the hypothesis that the underlying genes are homologues of Drosophila TRP (transient receptor potential). Direct evidence exists for roles of TRPC1, TRPC4/5, TRPC6, TRPV2, TRPP1 and TRPP2, and more are likely to be added soon. Some of these TRP proteins respond to a multiplicity of activation signals--promiscuity of gating that could enable a variety of context-dependent functions. We would seem to be witnessing the first phase of the molecular delineation of these cationic channels, something that should prove a leap forward for strategies aimed at developing new selective pharmacological agents and understanding the activation mechanisms and functions of these channels in physiological systems.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmmed GU, Mehta D, Vogel S, Holinstat M, Paria BC, Tiruppathi C, Malik AB. Protein kinase C-α phosphorylates the TRPC1 channel and regulates store-operated Ca2+ entry in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:20941–20949. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

