Regulation of tissue oxygen levels in the mammalian lens
- PMID: 15272034
- PMCID: PMC1665185
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.068619
Regulation of tissue oxygen levels in the mammalian lens
Abstract
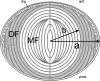
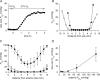
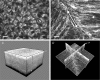
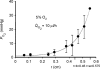
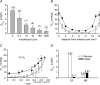
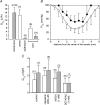
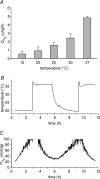
Opacification of the lens nucleus is a major cause of blindness and is thought to result from oxidation of key cellular components. Thus, long-term preservation of lens clarity may depend on the maintenance of hypoxia in the lens nucleus. We mapped the distribution of dissolved oxygen within isolated bovine lenses and also measured the rate of oxygen consumption (QO2) by lenses, or parts thereof. To assess the contribution of mitochondrial metabolism to the lens oxygen budget, we tested the effect of mitochondrial inhibitors on (QO2) and partial pressure of oxygen (PO2). The distribution of mitochondria was mapped in living lenses by 2-photon microscopy. We found that a steep gradient of PO2 was maintained within the tissue, leading to PO2 < 2 mmHg in the core. Mitochondrial respiration accounted for approximately 90% of the oxygen consumed by the lens; however, PO2 gradients extended beyond the boundaries of the mitochondria-containing cell layer, indicating the presence of non-mitochondrial oxygen consumers. Time constants for oxygen consumption in various regions of the lens and an effective oxygen diffusion coefficient were calculated from a diffusion-consumption model. Typical values were 3 x 10(-5) cm(2) s(-1) for the effective diffusion coefficient and a 5 min time constant for oxygen consumption. Surprisingly, the calculated time constants did not differ between differentiating fibres (DF) that contained mitochondria and mature fibres (MF) that did not. Based on these parameters, DF cells were responsible for approximately 88% of lens oxygen consumption. A modest reduction in tissue temperature resulted in a marked decrease in (QO2) and the subsequent flooding of the lens core with oxygen. This phenomenon may be of clinical relevance because cold, oxygen-rich solutions are often infused into the eye during intraocular surgery. Such procedures are associated with a strikingly high incidence of postsurgical nuclear cataract.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Estimation of human corneal oxygen consumption by noninvasive measurement of tear oxygen tension while wearing hydrogel lenses.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002 Feb;43(2):371-6. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002. PMID: 11818379
-
Oxygen distribution in the rabbit eye and oxygen consumption by the lens.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006 Apr;47(4):1571-80. doi: 10.1167/iovs.05-1475. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006. PMID: 16565394
-
Oxygen tension in the rabbit lens and vitreous before and after vitrectomy.Exp Eye Res. 2004 May;78(5):917-24. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2004.01.003. Exp Eye Res. 2004. PMID: 15051473
-
[The oxidative stress in the cataract formation].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 1995 Dec;99(12):1303-41. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 1995. PMID: 8571853 Review. Japanese.
-
Impact of diffusional oxygen transport on oxidative metabolism in the heart.Jpn J Physiol. 1998 Aug;48(4):243-52. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.48.243. Jpn J Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9757140 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization and functional expression of the natriuretic peptide system in human lens epithelial cells.Mol Vis. 2010 Apr 9;16:630-8. Mol Vis. 2010. PMID: 20700369 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of age on lens transport.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013 Nov 1;54(12):7174-87. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-12593. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013. PMID: 24065810 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of shear wave elastography for evaluating lens stiffness in patients with age-related cataracts: A quantitative analysis.Heliyon. 2024 May 31;10(11):e32255. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32255. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38882265 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of long-range chromatin contacts, compartments and looping between mouse embryonic stem cells, lens epithelium and lens fibers.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2024 Apr 20;17(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13072-024-00533-x. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2024. PMID: 38643244 Free PMC article.
-
Aggregation of lens crystallins in an in vivo hyperbaric oxygen guinea pig model of nuclear cataract: dynamic light-scattering and HPLC analysis.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005 Dec;46(12):4641-51. doi: 10.1167/iovs.05-0843. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005. PMID: 16303961 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bantseev VL, Herbert KL, Trevithick JR, Sivak JG. Mitochondria of rat lenses: distribution near and at the sutures. Curr Eye Res. 1999;19:506–516. - PubMed
-
- Barbazetto IA, Liang J, Chang S, Zheng L, Spector A, Dillon JP. Oxygen tension in the rabbit lens and vitreous before and after vitrectomy. Exp Eye Res. 2004;78:917–924. - PubMed
-
- Bassnett S. Lens organelle degradation. Exp Eye Res. 2002;74:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Bassnett S, Beebe DC. Coincident loss of mitochondria and nuclei during lens fiber cell differentiation. Dev Dyn. 1992;194:85–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

