Neurotransmitter modulation of extracellular H+ fluxes from isolated retinal horizontal cells of the skate
- PMID: 15272044
- PMCID: PMC1665295
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.065425
Neurotransmitter modulation of extracellular H+ fluxes from isolated retinal horizontal cells of the skate
Abstract
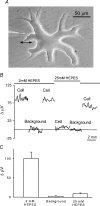
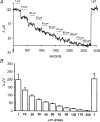
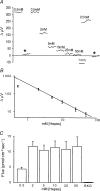
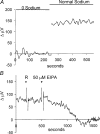
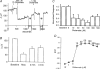
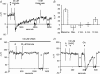
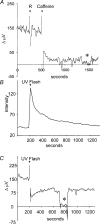
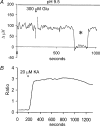
Self-referencing H(+)-selective microelectrodes were used to measure extracellular H(+) fluxes from horizontal cells isolated from the skate retina. A standing H(+) flux was detected from quiescent cells, indicating a higher concentration of free hydrogen ions near the extracellular surface of the cell as compared to the surrounding solution. The standing H(+) flux was reduced by removal of extracellular sodium or application of 5-(N-ethyl-N-isopropyl) amiloride (EIPA), suggesting activity of a Na(+)-H(+) exchanger. Glutamate decreased H(+) flux, lowering the concentration of free hydrogen ions around the cell. AMPA/kainate receptor agonists mimicked the response, and the AMPA/kainate receptor antagonist 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX) eliminated the effects of glutamate and kainate. Metabotropic glutamate agonists were without effect. Glutamate-induced alterations in H(+) flux required extracellular calcium, and were abolished when cells were bathed in an alkaline Ringer solution. Increasing intracellular calcium by photolysis of the caged calcium compound NP-EGTA also altered extracellular H(+) flux. Immunocytochemical localization of the plasmalemma Ca(2+)-H(+)-ATPase (PMCA pump) revealed intense labelling within the outer plexiform layer and on isolated horizontal cells. Our results suggest that glutamate modulation of H(+) flux arises from calcium entry into cells with subsequent activation of the plasmalemma Ca(2+)-H(+)-ATPase. These neurotransmitter-induced changes in extracellular pH have the potential to play a modulatory role in synaptic processing in the outer retina. However, our findings argue against the hypothesis that hydrogen ions released by horizontal cells normally act as the inhibitory feedback neurotransmitter onto photoreceptor synaptic terminals to create the surround portion of the centre-surround receptive fields of retinal neurones.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Modulation of extracellular proton fluxes from retinal horizontal cells of the catfish by depolarization and glutamate.J Gen Physiol. 2007 Aug;130(2):169-82. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200709737. J Gen Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17664345 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological characterization, localization, and regulation of ionotropic glutamate receptors in skate horizontal cells.Vis Neurosci. 2009 Jul-Aug;26(4):375-87. doi: 10.1017/S0952523809990149. Epub 2009 Aug 14. Vis Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19678977
-
Activation of retinal glial (Müller) cells by extracellular ATP induces pronounced increases in extracellular H+ flux.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 21;13(2):e0190893. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190893. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29466379 Free PMC article.
-
Sources of protons and a role for bicarbonate in inhibitory feedback from horizontal cells to cones in Ambystoma tigrinum retina.J Physiol. 2016 Nov 15;594(22):6661-6677. doi: 10.1113/JP272533. Epub 2016 Jul 21. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27345444 Free PMC article.
-
Distinctive patterns of alterations in proton efflux from goldfish retinal horizontal cells monitored with self-referencing H⁺-selective electrodes.Eur J Neurosci. 2012 Oct;36(8):3040-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2012.08226.x. Epub 2012 Jul 19. Eur J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22809323 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Depolarization of isolated horizontal cells of fish acidifies their immediate surrounding by activating V-ATPase.J Physiol. 2007 Dec 1;585(Pt 2):401-12. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.142646. Epub 2007 Oct 11. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17932147 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid rise of extracellular pH evoked by neural activity is generated by the plasma membrane calcium ATPase.J Neurophysiol. 2010 Feb;103(2):667-76. doi: 10.1152/jn.00948.2009. Epub 2009 Nov 25. J Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 19939954 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of extracellular proton fluxes from retinal horizontal cells of the catfish by depolarization and glutamate.J Gen Physiol. 2007 Aug;130(2):169-82. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200709737. J Gen Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17664345 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium dynamics and regulation in horizontal cells of the vertebrate retina: lessons from teleosts.J Neurophysiol. 2017 Feb 1;117(2):523-536. doi: 10.1152/jn.00585.2016. Epub 2016 Nov 2. J Neurophysiol. 2017. PMID: 27832601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ion-selective self-referencing probes for measuring specific ion flux.Commun Integr Biol. 2011 Sep;4(5):524-7. doi: 10.4161/cib.16182. Epub 2011 Sep 1. Commun Integr Biol. 2011. PMID: 22046453 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ammann D, Oesch U, Buhrer T, Simon W. Design of ionophores for ion-selective microsensors. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1987;65:879–884. - PubMed
-
- Arif I, Newman IA, Keenylside N. Proton flux measurements from tissues in buffered solution. Plant Cell Environ. 1995;18:1319–1324.
-
- Ayoub GS, Dorst K. Imaging of glutamate release from the goldfish retinal slice. Vision Res. 1998;38:2909–2912. 10.1016/S0042-6989(98)00103-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

