Chk1, but not Chk2, inhibits Cdc25 phosphatases by a novel common mechanism
- PMID: 15272308
- PMCID: PMC514503
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600328
Chk1, but not Chk2, inhibits Cdc25 phosphatases by a novel common mechanism
Abstract
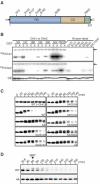
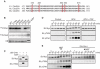
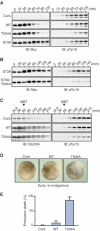
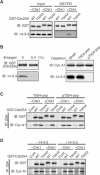
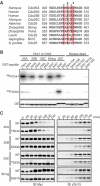
Cdc25 phosphatases activate cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) and thereby promote cell cycle progression. In vertebrates, Chk1 and Chk2 phosphorylate Cdc25A at multiple N-terminal sites and target it for rapid degradation in response to genotoxic stress. Here we show that Chk1, but not Chk2, phosphorylates Xenopus Cdc25A at a novel C-terminal site (Thr504) and inhibits it from C-terminally interacting with various Cdk-cyclin complexes, including Cdk1-cyclin A, Cdk1-cyclin B, and Cdk2-cyclin E. Strikingly, this inhibition, rather than degradation itself, of Cdc25A is essential for the Chk1-induced cell cycle arrest and the DNA replication checkpoint in early embryos. 14-3-3 proteins bind to Chk1-phosphorylated Thr504, but this binding is not required for the inhibitory effect of Thr504 phosphorylation. A C-terminal site presumably equivalent to Thr504 exists in all known Cdc25 family members from yeast to humans, and its phosphorylation by Chk1 (but not Chk2) can also inhibit all examined Cdc25 family members from C-terminally interacting with their Cdk-cyclin substrates. Thus, Chk1 but not Chk2 seems to inhibit virtually all Cdc25 phosphatases by a novel common mechanism.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Differential roles for checkpoint kinases in DNA damage-dependent degradation of the Cdc25A protein phosphatase.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jul 11;283(28):19322-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802474200. Epub 2008 May 13. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18480045 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Cdc2/cyclin B activation in Xenopus egg extracts via inhibitory phosphorylation of Cdc25C phosphatase by Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein [corrected] kinase II.Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Oct;14(10):4003-14. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-02-0061. Epub 2003 Jul 11. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 14517314 Free PMC article.
-
SCFbeta-TRCP links Chk1 signaling to degradation of the Cdc25A protein phosphatase.Genes Dev. 2003 Dec 15;17(24):3062-74. doi: 10.1101/gad.1157503. Epub 2003 Dec 17. Genes Dev. 2003. PMID: 14681206 Free PMC article.
-
Chk1 versus Cdc25: chking one's levels of cellular proliferation.Cell Cycle. 2004 Nov;3(11):1355-7. doi: 10.4161/cc.3.11.1225. Epub 2004 Nov 10. Cell Cycle. 2004. PMID: 15483403 Review.
-
The multiple checkpoint functions of CHK1 and CHK2 in maintenance of genome stability.Front Biosci. 2008 May 1;13:5016-29. doi: 10.2741/3060. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 18508566 Review.
Cited by
-
Chk1 Activation Protects Rad9A from Degradation as Part of a Positive Feedback Loop during Checkpoint Signalling.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 11;10(12):e0144434. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144434. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26658951 Free PMC article.
-
Chk1 Inhibition of the Replication Factor Drf1 Guarantees Cell-Cycle Elongation at the Xenopus laevis Mid-blastula Transition.Dev Cell. 2017 Jul 10;42(1):82-96.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.06.010. Dev Cell. 2017. PMID: 28697335 Free PMC article.
-
KRCC1, a modulator of the DNA damage response.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Oct 28;50(19):11028-11039. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac890. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 36243983 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-TrCP recognizes a previously undescribed nonphosphorylated destruction motif in Cdc25A and Cdc25B phosphatases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 May 3;102(18):6279-84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0501873102. Epub 2005 Apr 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15845771 Free PMC article.
-
Redundant pathways for Cdc2 activation in Xenopus oocyte: either cyclin B or Mos synthesis.EMBO Rep. 2006 Mar;7(3):321-5. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400611. Epub 2005 Dec 16. EMBO Rep. 2006. PMID: 16374506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham RT (2001) Cell cycle checkpoint signaling through the ATM and ATR kinases. Genes Dev 15: 2177–2196 - PubMed
-
- Barlow C, Hirotsune S, Paylor R, Liyanage M, Eckhaus M, Collins F, Shiloh Y, Crawley JN, Ried T, Tagle D, Wynshaw-Boris A (1996) ATM-deficient mice: a paradigm of ataxia telangiectasia. Cell 86: 159–171 - PubMed
-
- Bartek J, Lukas J (2003) Chk1 and Chk2 kinases in checkpoint control and cancer. Cancer Cell 3: 421–429 - PubMed
-
- Blasina A, Weyer IV, Laus MC, Luyten WHML, Parker AE, McGowan CH (1999) A human homologue of the checkpoint kinase Cds1 directly inhibits Cdc25 phosphatase. Curr Biol 9: 1–10 - PubMed
-
- Bulavin DV, Higashimoto Y, Popoff IJ, Gaarde A, Basrur V, Potapova O, Appella E, Fornace AJ (2001) Initiation of a G2/M checkpoint after ultraviolet radiation requires p38 kinase. Nature 411: 102–107 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

