Role of beta-lactamases and porins in resistance to ertapenem and other beta-lactams in Klebsiella pneumoniae
- PMID: 15273152
- PMCID: PMC478483
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.48.8.3203-3206.2004
Role of beta-lactamases and porins in resistance to ertapenem and other beta-lactams in Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
High-level resistance to ertapenem was produced by beta-lactamases of groups 1, 2f, and 3 in a strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae deficient in Omp35 and Omp36. From a wild-type strain producing ACT-1 beta-lactamase, ertapenem-resistant mutants for which the ertapenem MICs were up to 128 microg/ml and expression of outer membrane proteins was diminished could be selected.
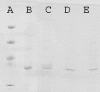
Figures
References
-
- Baucheron, S., H. Imberechts, E. Chaslus-Dancla, and A. Cloeckaert. 2002. The AcrB multidrug transporter plays a major role in high-level fluoroquinolone resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium phage type DT204. Microb. Drug Resist. 8:281-289. - PubMed
-
- Bradford, P. A., C. Urban, N. Mariano, S. J. Projan, J. J. Rahal, and K. Bush. 1997. Imipenem resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae is associated with the combination of ACT-1, a plasmid-mediated AmpC β-lactamase, and the loss of an outer membrane protein. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 41:563-569. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

