Systemic delivery of genes to striated muscles using adeno-associated viral vectors
- PMID: 15273747
- PMCID: PMC1365046
- DOI: 10.1038/nm1085
Systemic delivery of genes to striated muscles using adeno-associated viral vectors
Abstract
A major obstacle limiting gene therapy for diseases of the heart and skeletal muscles is an inability to deliver genes systemically to muscles of an adult organism. Systemic gene transfer to striated muscles is hampered by the vascular endothelium, which represents a barrier to distribution of vectors via the circulation. Here we show the first evidence of widespread transduction of both cardiac and skeletal muscles in an adult mammal, after a single intravenous administration of recombinant adeno-associated virus pseudotype 6 vectors. The inclusion of vascular endothelium growth factor/vascular permeability factor, to achieve acute permeabilization of the peripheral microvasculature, enhanced tissue transduction at lower vector doses. This technique enabled widespread muscle-specific expression of a functional micro-dystrophin in the skeletal muscles of dystrophin-deficient mdx mice, which model Duchenne muscular dystrophy. We propose that these methods may be applicable for systemic delivery of a wide variety of genes to the striated muscles of adult mammals.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
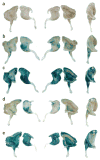
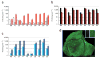

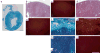
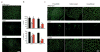
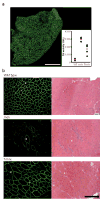
Comment in
-
Gene delivery goes global.Nat Med. 2004 Aug;10(8):782-3. doi: 10.1038/nm0804-782. Nat Med. 2004. PMID: 15286775 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hoshijima M, et al. Chronic suppression of heart-failure progression by a pseudophosphorylated mutant of phospholamban via in vivo cardiac rAAV gene delivery. Nat Med. 2002;8:864–871. - PubMed
-
- Musaro A, et al. Localized Igf-1 transgene expression sustains hypertrophy and regeneration in senescent skeletal muscle. Nat Genet. 2001;27:195–200. - PubMed
-
- Harper SQ, et al. Modular flexibility of dystrophin: implications for gene therapy of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nat Med. 2002;8:253–261. - PubMed
-
- Greelish JP, et al. Stable restoration of the sarcoglycan complex in dystrophic muscle perfused with histamine and a recombinant adeno-associated viral vector. Nat Med. 1999;5:439–443. - PubMed
-
- Bridges CR, et al. Global cardiac-specific transgene expression using cardiopulmonary bypass with cardiac isolation. Ann Thorac Surg. 2002;73:1939–1946. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

