Anandamide acts as a vasodilator of dural blood vessels in vivo by activating TRPV1 receptors
- PMID: 15277315
- PMCID: PMC1575202
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705896
Anandamide acts as a vasodilator of dural blood vessels in vivo by activating TRPV1 receptors
Abstract
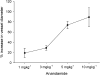
Migraine pathophysiology is believed to involve the release of neuropeptides via the activation of trigeminal afferents that innervate the cranial vasculature. Anandamide, the endogenous ligand to the cannabinoid receptor, is able to inhibit neurogenic dural vasodilatation, calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)-induced and nitric oxide-induced dural vessel dilation in the intravital microscopy model. In an in vitro setting anandamide is also able to activate the vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) receptor and cause vasodilation, via the release of CGRP. In this study we used intravital microscopy to study whether anandamide behaves as a TRPV1 receptor agonist in the trigeminovascular system. We examined if anandamide-induced dural vasodilation involves CGRP release that can be reversed by the CGRP receptor antagonist, CGRP(8-37), and whether like capsaicin the anandamide effect could be reversed by the TRPV1 receptor antagonist, capsazepine. Anandamide 1 (19+/-9%, n=12), 3 (29+/-5%, n=37), 5 (74+/-7%, n=13) and 10 mg kg(-1) (89+/-18%, n=6) was able to cause a dose-dependent increase in dural vessel diameter. Capsazepine (3 mg kg(-1), t(5)=6.2, P<0.05) and CGRP(8-37) (300 micrograms kg(-1), t(6)=11.1, P<0.05) attenuated the anandamide-induced dural vessel dilation when compared to control (Student's paired t-test). AM251 (3 mg kg(-1)), a cannabinoid type 1 (CB(1)) receptor antagonist, was unable to reverse this anandamide-induced dilation. The study demonstrates that anandamide acts as a TRPV1 receptor agonist in the trigeminovascular system, activating TRPV1 receptors that promote CGRP release and cause vasodilation independent of any action at the CB(1) receptor. Anandamide has been shown previously to inhibit trigeminovascular neurons and prevent vasodilation, through an action at CB(1) receptors.
Figures


References
-
- ADAMS I.B., COMPTON D.R., MARTIN B.R. Assessment of anandamide interaction with the cannabinoid brain receptor: SR 141716A antagonism studies in mice and autoradiographic analysis of receptor binding in rat brain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998;284:1209–1217. - PubMed
-
- AHLUWALIA J., URBAN L., BEVAN S., NAGY I. Anandamide regulates neuropeptide release from capsaicin-sensitive primary sensory neurons by activating both the cannabinoid 1 receptor and the vanilloid receptor 1 in vitro. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003;17:2611–2618. - PubMed
-
- AKERMAN S., KAUBE H., GOADSBY P.J. Anandamide is able to inhibit trigeminal neurons using an in vivo model of trigeminovascular-mediated nociception. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004;309:56–63. - PubMed
-
- CHAHL L.A., LYNCH A.M. The acute effects of capsaicin on the cardiovascular system. Acta. Physiol. Hung. 1987;69:413–419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

