Rpe65 Leu450Met variant is associated with reduced levels of the retinal pigment epithelium lipofuscin fluorophores A2E and iso-A2E
- PMID: 15277666
- PMCID: PMC511036
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0403499101
Rpe65 Leu450Met variant is associated with reduced levels of the retinal pigment epithelium lipofuscin fluorophores A2E and iso-A2E
Abstract
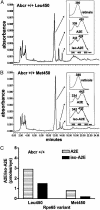
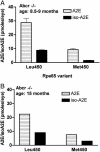
There is a growing body of evidence that the nondegradable fluorophores that accumulate as the lipofuscin of retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) are involved in mechanisms leading to the degeneration of RPE in macular degeneration. Most of the constituents of RPE lipofuscin are inadvertent products of the retinoid visual cycle, the enzymatic pathway by which the 11-cis-retinal chromophore of rhodopsin is generated. Indeed, a major constituent of RPE lipofuscin, the pyridinium bisretinoid A2E, is a diretinal conjugate that forms in photoreceptor cells and is deposited in RPE cells as a consequence of the phagocytosis of the outer segment membrane by RPE cells. Given the adverse effects of A2E, there is considerable interest in combating its deposition so as to protect against vision loss. These efforts, however, necessitate an understanding of factors that modulate its formation. Here we show that an amino acid variant in murine Rpe65, a visual-cycle protein required for the regeneration of 11-cis-retinal, is associated with reduced A2E accumulation.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

