Node retrieval in axillary lymph node dissections: recommendations for minimum numbers to be confident about node negative status
- PMID: 15280406
- PMCID: PMC1770384
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.2003.015560
Node retrieval in axillary lymph node dissections: recommendations for minimum numbers to be confident about node negative status
Abstract
Aims: To determine the minimum number of lymph nodes needed in an axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) specimen to be confident that the axilla is free from metastases.
Methods: The Edinburgh Breast Unit selects patients with large and high grade tumours for ALND; 609 consecutive ALNDs performed between October 1999 and December 2002 were reviewed. Full data about the underlying invasive breast cancer were available for 520 patients. Data were collected regarding number of positive nodes and total number of nodes collected, tumour size and grade, and presence of lymphovascular invasion.
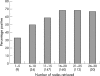
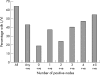
Results: Axillary node metastases were seen in 64% of patients. The mean number of positive nodes found was 3.56, with a mean of 17.9 nodes collected. The highest proportion of patients with lymph node metastases were in the group with 16-20 nodes recovered/specimen (68%); specimens with >20 nodes recovered did not have a higher rate of nodal involvement. There was a significant difference between the proportion of metastasis positive specimens in those with 1-15 nodes recovered (58.5%) and those with 16 or more recovered (69.1%). A linear association test showed a direct correlation between the number of nodes collected and presence of node metastasis (p = 0.0005).
Conclusions: Although there is no minimum number of nodes that should be recovered in an ALND specimen, 16 nodes should be regarded as a target to ensure a high level of confidence that the nodes are negative. Node positivity in an ALND specimen appears to obey the law of diminishing returns.
Figures
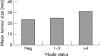
References
-
- Bonadonna G, Hortobagyi GN, Gianni AM. Textbook of breast cancer, a clinical guide to therapy. 2nd ed. London: Martin Dunitz, 2001.
-
- Golshirsh A, Wood WC, Senn H-J, et al. Meeting highlights international consensus panel on the treatment of primary breast cancer. J Natl Caner Inst 1995;87:1441–5. - PubMed
-
- Henson De, Ries L, Freedman LS, et al. Relationship among outcome, stage of disease and histologic grade for 22,616 cases of breast cancer: the basis for a prognostic index. Cancer 1991;68:2142–9. - PubMed
-
- Fisher ER, Anderson S, Redmond C, et al. Pathologic findings from the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast Project Protocol B-06: 10-year pathologic and clinical prognostic discriminants. Cancer 1993;71:2507–14. - PubMed
-
- Veronesi U, Galimberti V, Zurrida S, et al. Prognostic significance of number and level of axillary nodal metastases in breast cancer. Breast 1993;2:224–8.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
