Herpes simplex virus 1 has multiple mechanisms for blocking virus-induced interferon production
- PMID: 15280450
- PMCID: PMC479070
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.16.8411-8420.2004
Herpes simplex virus 1 has multiple mechanisms for blocking virus-induced interferon production
Abstract
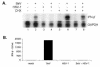
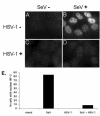
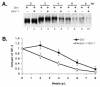
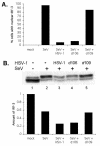
In response to viral infection, host cells elicit a number of responses, including the expression of alpha/beta interferon (IFN-alpha/beta). In these cells, IFN regulatory factor-3 (IRF-3) undergoes a sequence of posttranslational modifications that allow it to act as a potent transcriptional coactivator of specific IFN genes, including IFN-beta. We investigated the mechanisms by which herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) inhibits the production of IFN-beta mediated by the IRF-3 signaling pathway. Here, we show that HSV-1 infection can block the accumulation of IFN-beta triggered by Sendai virus (SeV) infection. Our results indicate that HSV-1 infection blocks the nuclear accumulation of activated IRF-3 but does not block the initial virus-induced phosphorylation of IRF-3. The former effect was at least partly mediated by increased turnover of IRF-3 in HSV-1-infected cells. Using mutant viruses, we determined that the immediate-early protein ICP0 was necessary for the inhibition of IRF-3 nuclear accumulation. Expression of ICP0 also had the ability to reduce IFN-beta production induced by SeV infection. ICP0 has been shown previously to play a role in HSV-1 sensitivity to IFN and in the inhibition of antiviral gene production. However, we observed that an ICP0 mutant virus still retained the ability to inhibit the production of IFN-beta. These results argue that HSV-1 has multiple mechanisms to inhibit the production of IFN-beta, providing additional ways in which HSV-1 can block the IFN-mediated host response.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Herpes simplex virus 1-encoded tegument protein VP16 abrogates the production of beta interferon (IFN) by inhibiting NF-κB activation and blocking IFN regulatory factor 3 to recruit its coactivator CBP.J Virol. 2013 Sep;87(17):9788-801. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01440-13. Epub 2013 Jul 3. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23824799 Free PMC article.
-
Recruitment of activated IRF-3 and CBP/p300 to herpes simplex virus ICP0 nuclear foci: Potential role in blocking IFN-beta induction.Virology. 2007 Apr 10;360(2):305-21. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.10.028. Epub 2006 Nov 28. Virology. 2007. PMID: 17126870 Free PMC article.
-
The Ebola virus VP35 protein inhibits activation of interferon regulatory factor 3.J Virol. 2003 Jul;77(14):7945-56. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.14.7945-7956.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12829834 Free PMC article.
-
On the role of IRF in host defense.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2002 Jan;22(1):59-71. doi: 10.1089/107999002753452665. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2002. PMID: 11846976 Review.
-
Mechanisms employed by herpes simplex virus 1 to inhibit the interferon response.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009 Sep;29(9):599-607. doi: 10.1089/jir.2009.0074. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009. PMID: 19694546 Review.
Cited by
-
Herpes simplex virus 1-encoded tegument protein VP16 abrogates the production of beta interferon (IFN) by inhibiting NF-κB activation and blocking IFN regulatory factor 3 to recruit its coactivator CBP.J Virol. 2013 Sep;87(17):9788-801. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01440-13. Epub 2013 Jul 3. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23824799 Free PMC article.
-
The Us3 Protein of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Inhibits T Cell Signaling by Confining Linker for Activation of T Cells (LAT) Activation via TRAF6 Protein.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jun 19;290(25):15670-15678. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.646422. Epub 2015 Apr 23. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25907557 Free PMC article.
-
The Race between Host Antiviral Innate Immunity and the Immune Evasion Strategies of Herpes Simplex Virus 1.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2020 Sep 30;84(4):e00099-20. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00099-20. Print 2020 Nov 18. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32998978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of interferon regulatory factor 3 in type I interferon responses in rotavirus-infected dendritic cells and fibroblasts.J Virol. 2007 Mar;81(6):2758-68. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01555-06. Epub 2007 Jan 10. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17215281 Free PMC article.
-
Infection with herpes simplex type 1-based amplicon vectors results in an IRF3/7-dependent, TLR-independent activation of the innate antiviral response in primary human fibroblasts.J Gen Virol. 2009 Sep;90(Pt 9):2209-20. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.012203-0. Epub 2009 Jun 10. J Gen Virol. 2009. PMID: 19515829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bandyopadhyay, S. K., G. T. Leonard, Jr., T. Bandyopadhyay, G. R. Stark, and G. C. Sen. 1995. Transcriptional induction by double-stranded RNA is mediated by interferon-stimulated response elements without activation of interferon-stimulated gene factor 3. J. Biol. Chem. 270:19624-19629. - PubMed
-
- Biron, C. A., and G. C. Sen. 2001. Interferons and other cytokines, p. 321-351. In D. M. Knipe and P. M. Howley (ed.), Fields virology, 4th ed., vol. 1. Lippincott/The Williams & Wilkins Co., Philadelphia, Pa.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

