Spirodiketopiperazine-based CCR5 inhibitor which preserves CC-chemokine/CCR5 interactions and exerts potent activity against R5 human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in vitro
- PMID: 15280474
- PMCID: PMC479103
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.16.8654-8662.2004
Spirodiketopiperazine-based CCR5 inhibitor which preserves CC-chemokine/CCR5 interactions and exerts potent activity against R5 human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in vitro
Abstract
We identified a novel spirodiketopiperazine (SDP) derivative, AK602/ONO4128/GW873140, which specifically blocked the binding of macrophage inflammatory protein 1alpha (MIP-1alpha) to CCR5 with a high affinity (K(d) of approximately 3 nM), potently blocked human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120/CCR5 binding and exerted potent activity against a wide spectrum of laboratory and primary R5 HIV-1 isolates, including multidrug-resistant HIV-1 (HIV-1(MDR)) (50% inhibitory concentration values of 0.1 to 0.6 nM) in vitro. AK602 competitively blocked the binding to CCR5 expressed on Chinese hamster ovary cells of two monoclonal antibodies, 45523, directed against multidomain epitopes of CCR5, and 45531, specific against the C-terminal half of the second extracellular loop (ECL2B) of CCR5. AK602, despite its much greater anti-HIV-1 activity than other previously published CCR5 inhibitors, including TAK-779 and SCH-C, preserved RANTES (regulated on activation normal T-cell expressed and secreted) and MIP-1beta binding to CCR5(+) cells and their functions, including CC-chemokine-induced chemotaxis and CCR5 internalization, while TAK-779 and SCH-C fully blocked the CC-chemokine/CCR5 interactions. Pharmacokinetic studies revealed favorable oral bioavailability in rodents. These data warrant further development of AK602 as a potential therapeutic for HIV-1 infection.
Figures




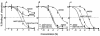


References
-
- Baba, M., O. Nishimura, N. Kanzaki, M. Okamoto, H. Sawada, Y. Iizawa, M. Shiraishi, Y. Aramaki, K. Okonogi, Y. Ogawa, K. Meguro, and M. Fujino. 1999. A small-molecule, nonpeptide CCR5 antagonist with highly potent and selective anti-HIV-1 activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96:5698-5703. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dean, M., M. Carrington, C. Winkler, G. A. Huttley, M. W. Smith, R. Allikmets, J. J. Goedert, S. P. Buchbinder, E. Vittinghoff, E. Gomperts, S. Donfield, D. Vlahov, R. Kaslow, A. Saah, C. Rinaldo, R. Detels, and S. J. O'Brien. 1996. Genetic restriction of HIV-1 infection and progression to AIDS by a deletion allele of the CKR5 structural gene. Hemophilia Growth and Development Study, Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study, Multicenter Hemophilia Cohort Study, San Francisco City Cohort, ALIVE Study. Science 273:1856-1862. - PubMed
-
- Dragic, T., A. Trkola, D. A. Thompson, E. G. Cormier, F. A. Kajumo, E. Maxwell, S. W. Lin, W. Ying, S. O. Smith, T. P. Sakmar, and J. P. Moore. 2000. A binding pocket for a small molecule inhibitor of HIV-1 entry within the transmembrane helices of CCR5. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:5639-5644. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Evans, E. A. 1974. Catalytic exchange in solution, p. 271-317. In Tritium and its compounds. Wiley and Sons, New York, N.Y.
-
- Fauci, A. S. 2003. HIV and AIDS: 20 years of science. Nat. Med. 9:839-843. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

