Chimeras of duck and heron hepatitis B viruses provide evidence for functional interactions between viral components of pregenomic RNA encapsidation
- PMID: 15280486
- PMCID: PMC479081
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.16.8780-8787.2004
Chimeras of duck and heron hepatitis B viruses provide evidence for functional interactions between viral components of pregenomic RNA encapsidation
Abstract
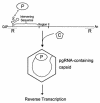
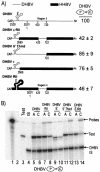
Packaging of hepadnavirus pregenomic RNA (pgRNA) into capsids, or encapsidation, requires several viral components. The viral polymerase (P) and the capsid subunit (C) are necessary for pgRNA encapsidation. Previous studies of duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV) indicated that two cis-acting sequences on pgRNA are required for encapsidation: epsilon, which is near the 5' end of pgRNA, and region II, located near the middle of pgRNA. Later studies suggested that the intervening sequence between these two elements may also make a contribution. It has been demonstrated for DHBV that epsilon interacts with P to facilitate encapsidation, but it is not known how other cis-acting sequences contribute to encapsidation. We analyzed chimeras of DHBV and a related virus, heron hepatitis B virus (HHBV), to gain insight into the interactions between the various viral components during pgRNA encapsidation. We learned that having epsilon and P derived from the same virus was not sufficient for high levels of encapsidation, implying that other viral interactions contribute to encapsidation. Chimeric analysis showed that a large sequence containing region II may interact with P and/or C for efficient encapsidation. Further analysis demonstrated that possibly an RNA-RNA interaction between the intervening sequence and region II facilitates pgRNA encapsidation. Together, these results identify functional interactions among various viral components that contribute to pgRNA encapsidation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of the cis-acting contributions to avian hepadnavirus RNA encapsidation.J Virol. 2002 Sep;76(18):9087-95. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.18.9087-9095.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12186892 Free PMC article.
-
Previously unsuspected cis-acting sequences for DNA replication revealed by characterization of a chimeric heron/duck hepatitis B virus.J Virol. 1996 Dec;70(12):8310-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.70.12.8310-8317.1996. J Virol. 1996. PMID: 8970950 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence- and structure-specific determinants in the interaction between the RNA encapsidation signal and reverse transcriptase of avian hepatitis B viruses.J Virol. 1997 Jul;71(7):4971-80. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.7.4971-4980.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9188560 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of the encapsidation signal of hepadnaviridae.J Viral Hepat. 1998 Nov;5(6):357-67. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2893.1998.00124.x. J Viral Hepat. 1998. PMID: 9857345 Review.
-
Molecular Basis of Encapsidation of Hepatitis C Virus Genome.Front Microbiol. 2018 Mar 7;9:396. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00396. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29563905 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating the hepatitis B virus life cycle using engineered reporter hepatitis B viruses.Cancer Sci. 2018 Jan;109(1):241-249. doi: 10.1111/cas.13440. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Cancer Sci. 2018. PMID: 29121422 Free PMC article.
-
A high level of mutation tolerance in the multifunctional sequence encoding the RNA encapsidation signal of an avian hepatitis B virus and slow evolution rate revealed by in vivo infection.J Virol. 2011 Sep;85(18):9300-13. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05005-11. Epub 2011 Jul 13. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21752921 Free PMC article.
-
C-terminal substitution of HBV core proteins with those from DHBV reveals that arginine-rich 167RRRSQSPRR175 domain is critical for HBV replication.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41087. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041087. Epub 2012 Jul 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22911745 Free PMC article.
-
Few basepairing-independent motifs in the apical half of the avian HBV ε RNA stem-loop determine site-specific initiation of protein-priming.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 2;7(1):7120. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07657-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28769080 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus replication.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Jan 7;13(1):48-64. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i1.48. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17206754 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Buscher, M., W. Reiser, H. Will, and H. Schaller. 1985. Transcripts and the putative RNA pregenome of duck hepatitis B virus: implications for reverse transcription. Cell 40:717-724. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

