Symmetry elements in DNA structure important for recognition/methylation by DNA [amino]-methyltransferases
- PMID: 15280508
- PMCID: PMC506800
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh712
Symmetry elements in DNA structure important for recognition/methylation by DNA [amino]-methyltransferases
Abstract
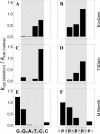
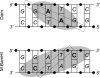
The phage T4Dam and EcoDam DNA-[adenine-N6] methyltransferases (MTases) methylate GATC palindromic sequences, while the BamHI DNA-[cytosine-N4] MTase methylates the GGATCC palindrome (which contains GATC) at the internal cytosine residue. We compared the ability of these enzymes to interact productively with defective duplexes in which individual elements were deleted on one chain. A sharp decrease in kcat was observed for all three enzymes if a particular element of structural symmetry was disrupted. For the BamHI MTase, integrity of the ATCC was critical, while an intact GAT sequence was necessary for the activity of T4Dam, and an intact GA was necessary for EcoDam. Theoretical alignment of the region of best contacts between the protein and DNA showed that in the case of a palindromic interaction site, a zone covering the 5'-symmetric residues is located in the major groove versus a zone of contact covering the 3'-symmetric residues in the minor groove. Our data fit a simple rule of thumb that the most important contacts are aligned around the methylation target base: if the target base is in the 5' half of the palindrome, the interaction between the enzyme and the DNA occurs mainly in the major groove; if it is in the 3' half, the interaction occurs mainly in the minor groove.
Figures
References
-
- Barras F. and Marinus,M.G. (1989) The great GATC: DNA methylation in E. coli. Trends Genet., 5, 139–143. - PubMed
-
- Cheng X. (1995) Structure and function of DNA methyltransferases. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct., 24, 293–318. - PubMed
-
- Wu J.C. and Santi,D.V. (1987) Kinetic and catalytic mechanism of HhaI methyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem., 262, 4778–4786. - PubMed
-
- Malone Th., Blumenthal,R.M. and Cheng,X. (1995) Structure-guided analysis reveals nine sequence motifs conserved among DNA amino-methyltransferases, and suggests a catalytic mechanism for these enzymes. J. Mol. Biol., 253, 618–632. - PubMed
-
- Jeltsch A. (2002) Beyond Watson and Crick: DNA methylation and molecular enzymology of DNA methyltransferases. Chembiochem, 3, 274–293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

