Persistent tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium current resulting from U-to-C RNA editing of an insect sodium channel
- PMID: 15280550
- PMCID: PMC511065
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0307695101
Persistent tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium current resulting from U-to-C RNA editing of an insect sodium channel
Abstract
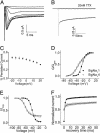
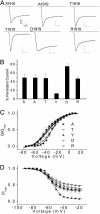
The persistent tetrodotoxin (TTX)-sensitive sodium current, detected in neurons of many regions of mammalian brains, is associated with many essential neuronal activities, including boosting of excitatory synaptic inputs, acceleration of firing rates, and promotion of oscillatory neuronal activities. However, the origin and molecular basis of the persistent current have remained controversial for decades. Here, we provide direct evidence that U-to-C RNA editing of an insect sodium channel transcript generates a sodium channel with a persistent current. We detected a persistent TTX-sensitive current in a splice variant of the cockroach sodium channel gene BgNa(v) (formerly para(CSMA)). Site-directed mutagenesis experiments revealed that an F-to-S change at the C-terminal domain of this variant was responsible for the persistent current. We demonstrated that this F-to-S change was the result of a U-to-C RNA editing event, which also occurred in the Drosophila para sodium channel transcript. Our work provides direct support for the hypothesis that posttranscriptional modification of a conventional transient sodium channel produces a persistent TTX-sensitive sodium channel.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RNA editing generates tissue-specific sodium channels with distinct gating properties.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jul 30;279(31):32554-61. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M402392200. Epub 2004 May 10. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15136570 Free PMC article.
-
[The role of tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channels in pain sensation studied on sns-knockout mice].Nihon Rinsho. 2001 Sep;59(9):1688-97. Nihon Rinsho. 2001. PMID: 11554037 Review. Japanese.
-
Contactin regulates the current density and axonal expression of tetrodotoxin-resistant but not tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium channels in DRG neurons.Eur J Neurosci. 2005 Jul;22(1):39-49. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04186.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16029194
-
Interactions of the C-11 hydroxyl of tetrodotoxin with the sodium channel outer vestibule.Biophys J. 2003 Jan;84(1):287-94. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74849-8. Biophys J. 2003. PMID: 12524282 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent Na-channels: origin and function. A review.Acta Biol Hung. 2008;59 Suppl:1-12. doi: 10.1556/ABiol.59.2008.Suppl.1. Acta Biol Hung. 2008. PMID: 18652365 Review.
Cited by
-
A knock-in model of human epilepsy in Drosophila reveals a novel cellular mechanism associated with heat-induced seizure.J Neurosci. 2012 Oct 10;32(41):14145-55. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2932-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23055484 Free PMC article.
-
RNA editing in P transposable element read-through transcripts in Drosophila melanogaster.Genetica. 2010 Dec;138(11-12):1119-26. doi: 10.1007/s10709-010-9499-z. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Genetica. 2010. PMID: 20886259
-
Distinct functional properties of sodium channel variants are associated with usage of alternative exons in Nilaparvata lugens.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2020 Mar;118:103292. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2019.103292. Epub 2019 Dec 4. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31811885 Free PMC article.
-
A distinct sodium channel voltage-sensor locus determines insect selectivity of the spider toxin Dc1a.Nat Commun. 2014 Jul 11;5:4350. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5350. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 25014760 Free PMC article.
-
First detection of a Vssc allele V1016G conferring a high level of insecticide resistance in Aedes albopictus collected from Europe (Italy) and Asia (Vietnam), 2016: a new emerging threat to controlling arboviral diseases.Euro Surveill. 2019 Jan;24(5):1700847. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2019.24.5.1700847. Euro Surveill. 2019. PMID: 30722810 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

