Spatiotemporal wavelet resampling for functional neuroimaging data
- PMID: 15281138
- PMCID: PMC6871944
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.20045
Spatiotemporal wavelet resampling for functional neuroimaging data
Abstract
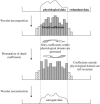
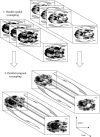
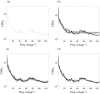
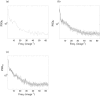
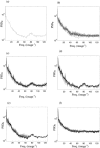
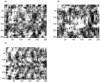
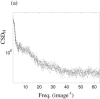
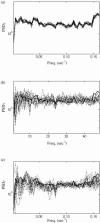
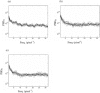
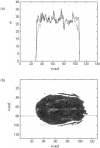
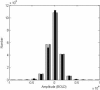
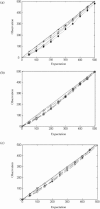
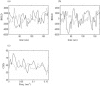
The study of dynamic interdependences between brain regions is currently a very active research field. For any connectivity study, it is important to determine whether correlations between two selected brain regions are statistically significant or only chance effects due to non-specific correlations present throughout the data. In this report, we present a wavelet-based non-parametric technique for testing the null hypothesis that the correlations are typical of the data set and not unique to the regions of interest. This is achieved through spatiotemporal resampling of the data in the wavelet domain. Two functional MRI data sets were analysed: (1) Data from 8 healthy human subjects viewing a checkerboard image, and (2) "Null" data obtained from 3 healthy human subjects, resting with eyes closed. It was demonstrated that constrained resampling of the data in the wavelet domain allows construction of bootstrapped data with four essential properties: (1) Spatial and temporal correlations within and between slices are preserved, (2) The irregular geometry of the intracranial images is maintained, (3) There is adequate type I error control, and (4) Expected experiment-induced correlations are identified. The limitations and possible extensions of the proposed technique are discussed.
Copyright 2004 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Andrzejak RG, Kraskov A, Stogbauer H, Mormann F, Kreuz T (2004): Bivariate surrogate techniques: necessity, strengths and caveats. Phys Rev E 68: 066202. - PubMed
-
- Brammer MJ, Bullmore ET, Simmons A, Williams SCR, Grasby PM, Howard RJ, Woodruff PWR, Rabe‐Hesketh S (1997): Generic brain activation in functional magnetic resonance imaging: A non‐parametric approach. Magnet Reson Imag 15: 763–770. - PubMed
-
- Breakspear M, Terry J (2002a): Detection and description of nonlinear interdependence in normal multichannel human EEG. Clin Neurophysiol 113: 735–753. - PubMed
-
- Breakspear M, Terry J (2002b): Topographic organisation of nonlinear interdependence in multichannel human EEG. Neuroimage 16: 822–825. - PubMed
-
- Breakspear M, Brammer MJ, Robinson PA (2003): Construction of multivariate surrogate sets from nonlinear data using the wavelet transform. Physica D 182: 1–22.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

