Biochemical enrichment and biophysical characterization of a taste receptor for L-arginine from the catfish, Ictalurus puntatus
- PMID: 15282034
- PMCID: PMC511074
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-5-25
Biochemical enrichment and biophysical characterization of a taste receptor for L-arginine from the catfish, Ictalurus puntatus
Abstract
Background: The channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus, is invested with a high density of cutaneous taste receptors, particularly on the barbel appendages. Many of these receptors are sensitive to selected amino acids, one of these being a receptor for L-arginine (L-Arg). Previous neurophysiological and biophysical studies suggested that this taste receptor is coupled directly to a cation channel and behaves as a ligand-gated ion channel receptor (LGICR). Earlier studies demonstrated that two lectins, Ricinus communis agglutinin I (RCA-I) and Phaseolus vulgaris Erythroagglutinin (PHA-E), inhibited the binding of L-Arg to its presumed receptor sites, and that PHA-E inhibited the L-Arg-stimulated ion conductance of barbel membranes reconstituted into lipid bilayers.
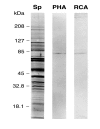
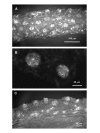
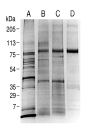
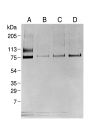
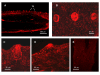
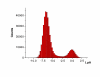
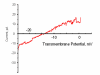
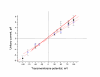
Results: Both PHA-E and RCA-I almost exclusively labeled an 82-84 kDa protein band of an SDS-PAGE of solubilized barbel taste epithelial membranes. Further, both rhodamine-conjugated RCA-I and polyclonal antibodies raised to the 82-84 kDa electroeluted peptides labeled the apical region of catfish taste buds. Because of the specificity shown by RCA-I, lectin affinity was chosen as the first of a three-step procedure designed to enrich the presumed LGICR for L-Arg. Purified and CHAPS-solubilized taste epithelial membrane proteins were subjected successively to (1), lectin (RCA-I) affinity; (2), gel filtration (Sephacryl S-300HR); and (3), ion exchange chromatography. All fractions from each chromatography step were evaluated for L-Arg-induced ion channel activity by reconstituting each fraction into a lipid bilayer. Active fractions demonstrated L-Arg-induced channel activity that was inhibited by D-arginine (D-Arg) with kinetics nearly identical to those reported earlier for L-Arg-stimulated ion channels of native barbel membranes reconstituted into lipid bilayers. After the final enrichment step, SDS-PAGE of the active ion channel protein fraction revealed a single band at 82-84 kDa which may be interpreted as a component of a multimeric receptor/channel complex.
Conclusions: The data are consistent with the supposition that the L-Arg receptor is a LGICR. This taste receptor remains active during biochemical enrichment procedures. This is the first report of enrichment of an active LGICR from the taste system of vertebrata.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The arginine taste receptor. Physiology, biochemistry, and immunohistochemistry.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998 Nov 30;855:134-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb10555.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998. PMID: 9929594
-
Amino acid-activated channels in the catfish taste system.Biophys J. 1998 Dec;75(6):2757-66. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(98)77719-7. Biophys J. 1998. PMID: 9826598 Free PMC article.
-
Differential localization of putative amino acid receptors in taste buds of the channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus.J Comp Neurol. 1996 Sep 9;373(1):129-38. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9861(19960909)373:1<129::AID-CNE11>3.0.CO;2-F. J Comp Neurol. 1996. PMID: 8876468
-
Transduction mechanisms for the taste of amino acids.Physiol Behav. 1991 May;49(5):899-904. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(91)90201-x. Physiol Behav. 1991. PMID: 1679559 Review.
-
The taste system of the channel catfish: from biophysics to behavior.Trends Neurosci. 1993 May;16(5):192-7. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90152-c. Trends Neurosci. 1993. PMID: 7685945 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of ligands for fish taste receptors.J Neurosci. 2007 May 23;27(21):5584-92. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0651-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17522303 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudogenization of a sweet-receptor gene accounts for cats' indifference toward sugar.PLoS Genet. 2005 Jul;1(1):27-35. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0010003. Epub 2005 Jul 25. PLoS Genet. 2005. PMID: 16103917 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of taste receptors.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(16):2669-83. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990566. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 23886383 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Witt M. Reutter, K. Miller, I.J. Morphology of the peripheral taste system. In: Doty RL, editor. Handbook of Olfaction and Gustation. Second. New York, Marcel Dekker, Inc.; 2003. pp. 651–677.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

