Fibroblast growth factor homologous factor 2B: association with Nav1.6 and selective colocalization at nodes of Ranvier of dorsal root axons
- PMID: 15282281
- PMCID: PMC6729706
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1628-04.2004
Fibroblast growth factor homologous factor 2B: association with Nav1.6 and selective colocalization at nodes of Ranvier of dorsal root axons
Abstract
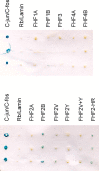
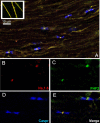
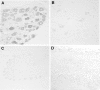
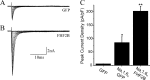
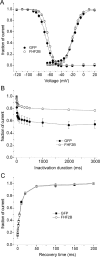
Voltage-gated sodium channels interact with cytosolic proteins that regulate channel trafficking and/or modulate the biophysical properties of the channels. Na(v)1.6 is heavily expressed at the nodes of Ranvier along adult CNS and PNS axons and along unmyelinated fibers in the PNS. In an initial yeast two-hybrid screen using the C terminus of Na(v)1.6 as a bait, we identified FHF2B, a member of the FGF homologous factor (FHF) subfamily, as an interacting partner of Na(v)1.6. Members of the FHF subfamily share approximately 70% sequence identity, and individual members demonstrate a cell- and tissue-specific expression pattern. FHF2 is abundantly expressed in the hippocampus and DRG neurons and colocalizes with Na(v)1.6 at mature nodes of Ranvier in myelinated sensory fibers in the dorsal root of the sciatic nerve. However, retinal ganglion cells and spinal ventral horn motor neurons show very low levels of FHF2 expression, and their axons exhibit no nodal FHF2 staining within the optic nerve and ventral root, respectively. Thus, FHF2 is selectively localized at nodes of dorsal root sensory but not ventral root motor axons. The coexpression of FHF2B and Na(v)1.6 in the DRG-derived cell line ND7/23 significantly increases the peak current amplitude and causes a 4 mV depolarizing shift of voltage-dependent inactivation of the channel. The preferential expression of FHF2B in sensory neurons may provide a basis for physiological differences in sodium currents that have been reported at the nodes of Ranvier in sensory versus motor axons.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Differential modulation of sodium channel Na(v)1.6 by two members of the fibroblast growth factor homologous factor 2 subfamily.Eur J Neurosci. 2006 May;23(10):2551-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.04789.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16817858
-
betaIV spectrin, a new spectrin localized at axon initial segments and nodes of ranvier in the central and peripheral nervous system.J Cell Biol. 2000 Nov 27;151(5):985-1002. doi: 10.1083/jcb.151.5.985. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11086001 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct repriming and closed-state inactivation kinetics of Nav1.6 and Nav1.7 sodium channels in mouse spinal sensory neurons.J Physiol. 2003 Sep 15;551(Pt 3):741-50. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.047357. Epub 2003 Jul 3. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12843211 Free PMC article.
-
Nodes of Ranvier come of age.Trends Neurosci. 2002 Jan;25(1):2-5. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(00)02006-3. Trends Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11801321 Review.
-
The local differentiation of myelinated axons at nodes of Ranvier.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003 Dec;4(12):968-80. doi: 10.1038/nrn1253. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14682359 Review.
Cited by
-
The fibroblast growth factor 14·voltage-gated sodium channel complex is a new target of glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3).J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 5;288(27):19370-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.445924. Epub 2013 May 2. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23640885 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast growth factor homologous factor 2 attenuates excitability of DRG neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2022 Nov 1;128(5):1258-1266. doi: 10.1152/jn.00361.2022. Epub 2022 Oct 12. J Neurophysiol. 2022. PMID: 36222860 Free PMC article.
-
FGF14 localization and organization of the axon initial segment.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013 Sep;56:393-403. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2013.07.008. Epub 2013 Jul 26. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23891806 Free PMC article.
-
Altered integration of excitatory inputs onto the basal dendrites of layer 5 pyramidal neurons in a mouse model of Fragile X syndrome.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Jan 10;120(2):e2208963120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2208963120. Epub 2023 Jan 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 36595706 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Inhibition of Wee1 Kinase Selectively Modulates the Voltage-Gated Na+ Channel 1.2 Macromolecular Complex.Cells. 2021 Nov 10;10(11):3103. doi: 10.3390/cells10113103. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831326 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akopian AN, Sivilotti L, Wood JN (1996) A tetrodotoxin-resistant voltage-gated sodium channel expressed by sensory neurons. Nature 379: 257-262. - PubMed
-
- Black JA, Dib-Hajj S, McNabola K, Jeste S, Rizzo MA, Kocsis JD, Waxman SG (1996) Spinal sensory neurons express multiple sodium channel alpha-subunit mRNAs. Mol Brain Res 43: 117-131. - PubMed
-
- Black JA, Renganathan M, Waxman SG (2002) Sodium channel Na(v)1.6 is expressed along nonmyelinated axons and it contributes to conduction. Mol Brain Res 105: 19-28. - PubMed
-
- Boiko T, Rasband MN, Levinson SR, Caldwell JH, Mandel G, Trimmer JS, Matthews G (2001) Compact myelin dictates the differential targeting of two sodium channel isoforms in the same axon. Neuron 30: 91-104. - PubMed
-
- Bostock H, Burke D, Hales JP (1994) Differences in behaviour of sensory and motor axons following release of ischaemia. Brain 117: 225-234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
