Oxidative stress sensor Keap1 functions as an adaptor for Cul3-based E3 ligase to regulate proteasomal degradation of Nrf2
- PMID: 15282312
- PMCID: PMC479737
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.16.7130-7139.2004
Oxidative stress sensor Keap1 functions as an adaptor for Cul3-based E3 ligase to regulate proteasomal degradation of Nrf2
Abstract
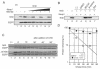
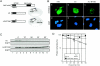
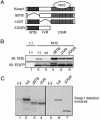
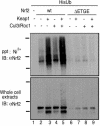
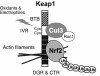
Transcription factor Nrf2 is a major regulator of genes encoding phase 2 detoxifying enzymes and antioxidant stress proteins in response to electrophilic agents and oxidative stress. In the absence of such stimuli, Nrf2 is inactive owing to its cytoplasmic retention by Keap1 and rapid degradation through the proteasome system. We examined the contribution of Keap1 to the rapid turnover of Nrf2 (half-life of less than 20 min) and found that a direct association between Keap1 and Nrf2 is required for Nrf2 degradation. In a series of domain function analyses of Keap1, we found that both the BTB and intervening-region (IVR) domains are crucial for Nrf2 degradation, implying that these two domains act to recruit ubiquitin-proteasome factors. Indeed, Cullin 3 (Cul3), a subunit of the E3 ligase complex, was found to interact specifically with Keap1 in vivo. Keap1 associates with the N-terminal region of Cul3 through the IVR domain and promotes the ubiquitination of Nrf2 in cooperation with the Cul3-Roc1 complex. These results thus provide solid evidence that Keap1 functions as an adaptor of Cul3-based E3 ligase. To our knowledge, Nrf2 and Keap1 are the first reported mammalian substrate and adaptor, respectively, of the Cul3-based E3 ligase system.
Figures



References
-
- Cope, G. A., and R. J. Deshaies. 2003. COP9 signalosome: a multifunctional regulator of SCF and other cullin-based ubiquitin ligases. Cell 114:663-671. - PubMed
-
- Dinkova-Kostova, A. T., W. D. Holtzclaw, R. N. Cole, K. Itoh, N. Wakabayashi, Y. Katoh, M. Yamamoto, and P. Talalay. 2002. Direct evidence that sulfhydryl groups of Keap1 are the sensors regulating induction of phase 2 enzymes that protect against carcinogens and oxidants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99:11908-11913. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Furukawa, M., Y. J. He, C. Borchers, and Y. Xiong. 2003. Targeting of protein ubiquitination by BTB-Cullin 3-Roc1 ubiquitin ligases. Nat. Cell Biol. 5:1001-1007. - PubMed
-
- Geyer, R., S. Wee, S. Anderson, J. Yates, and D. A. Wolf. 2003. BTB/POZ domain proteins are putative substrate adaptors for cullin 3 ubiquitin ligases. Mol. Cell 12:783-790. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
