The kinase Grk2 regulates Nedd4/Nedd4-2-dependent control of epithelial Na+ channels
- PMID: 15284439
- PMCID: PMC511069
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0402178101
The kinase Grk2 regulates Nedd4/Nedd4-2-dependent control of epithelial Na+ channels
Abstract
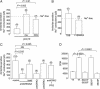
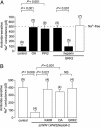
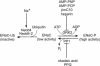
Epithelial Na(+) channels mediate the transport of Na across epithelia in the kidney, gut, and lungs and are required for blood pressure regulation. They are inhibited by ubiquitin protein ligases, such as Nedd4 and Nedd4-2, with loss of this inhibition leading to hypertension. Here, we report that these channels are maintained in the active state by the G protein-coupled receptor kinase, Grk2, which has been previously implicated in the development of essential hypertension. We also show that Grk2 phosphorylates the C terminus of the channel beta subunit and renders the channels insensitive to inhibition by Nedd4-2. This mechanism has not been previously reported to regulate epithelial Na(+) channels and provides a potential explanation for the observed association of Grk2 overactivity with hypertension. Here, we report a G protein-coupled receptor kinase regulating a membrane protein other than a receptor and provide a paradigm for understanding how the interaction between membrane proteins and ubiquitin protein ligases is controlled.
Figures

Similar articles
-
GRK2 interacts with and phosphorylates Nedd4 and Nedd4-2.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007 Aug 3;359(3):611-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.05.134. Epub 2007 May 29. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007. PMID: 17544362
-
Scoring of predicted GRK2 phosphorylation sites in Nedd4-2.Bioinformatics. 2006 Sep 15;22(18):2192-5. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl381. Epub 2006 Jul 14. Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16844705
-
Patch-clamp studies on epithelial sodium channels in salivary duct cells.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2002;36(2-3):105-13. doi: 10.1385/cbb:36:2-3:105. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2002. PMID: 12139396 Review.
-
Nedd4 mediates control of an epithelial Na+ channel in salivary duct cells by cytosolic Na+.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jun 9;95(12):7169-73. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.12.7169. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9618557 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Nedd4/Nedd4-like dependant ubiquitylation in epithelial transport processes.Pflugers Arch. 2003 Jun;446(3):334-8. doi: 10.1007/s00424-003-1027-x. Epub 2003 Apr 16. Pflugers Arch. 2003. PMID: 12698368 Review.
Cited by
-
Association Between Polymorphisms of ADRBK1 Gene and Plasma Renin Activity in Hypertensive Patients: A Case-Control Study.Med Sci Monit. 2016 Aug 24;22:2981-8. doi: 10.12659/msm.896579. Med Sci Monit. 2016. PMID: 27555048 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane transport: ionic environments, signal transduction, and development of therapeutic targets.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:581626. doi: 10.1155/2015/581626. Epub 2015 Apr 12. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25954754 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
NEDD4L in human tumors: regulatory mechanisms and dual effects on anti-tumor and pro-tumor.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Nov 9;14:1291773. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1291773. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38027016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predikin and PredikinDB: a computational framework for the prediction of protein kinase peptide specificity and an associated database of phosphorylation sites.BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 May 26;9:245. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-245. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18501020 Free PMC article.
-
The Epithelial Sodium Channel-An Underestimated Drug Target.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 24;24(9):7775. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097775. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175488 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rossier, B. C., Pradervand, S., Schild, L. & Hummler, E. (2002) Annu. Rev. Physiol. 64, 877-897. - PubMed
-
- Matsui, H., Grubb, B. R., Tarran, R., Randell, S. H., Gatzy, J. T., Davis, C. W. & Boucher, R. C. (1998) Cell 95, 1005-1015. - PubMed
-
- Snyder, P. M., Price, M. P., McDonald, F. J., Adams, C. M., Volk, K. A., Zeiher, B. G., Stokes, J. B. & Welsh, M. J. (1995) Cell 83, 969-978. - PubMed
-
- Mall, M., Grubb, B. R., Harkema, J. R., OíNeal, W. K. & Boucher, R. C. (2004) Nat. Med. 10, 487-493. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

