MicroRNA profiling reveals distinct signatures in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemias
- PMID: 15284443
- PMCID: PMC511048
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0404432101
MicroRNA profiling reveals distinct signatures in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemias
Abstract
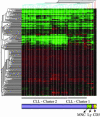
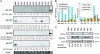
Little is known about the expression levels or function of micro-RNAs (miRNAs) in normal and neoplastic cells, although it is becoming clear that miRNAs play important roles in the regulation of gene expression during development [Ambros, V. (2003) Cell 113, 673-676; McManus, M. T. (2003) Semin. Cancer Biol. 13, 253-258]. We now report the genomewide expression profiling of miRNAs in human B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) by using a microarray containing hundreds of human precursor and mature miRNA oligonucleotide probes. This approach allowed us to identify significant differences in miRNome expression between CLL samples and normal CD5+ B cells; data were confirmed by Northern blot analyses and real-time RT-PCR. At least two distinct clusters of CLL samples can be identified that were associated with the presence or absence of Zap-70 expression, a predictor of early disease progression. Two miRNA signatures were associated with the presence or absence of mutations in the expressed Ig variableregion genes or with deletions at 13q14, respectively. These data suggest that miRNA expression patterns have relevance to the biological and clinical behavior of this leukemia.
Figures
References
-
- Moss, E. G. (2003) in MicroRNAs in Noncoding RNAs: Molecular Biology and Molecular Medicine), eds. Barciszewski, J. & Erdmann, V. (Landes Bioscience, Georgetown, TX), pp. 98–114.
-
- Bartel, D. P. (2004) Cell 116, 281–297. - PubMed
-
- Ambros, V. (2003) Cell 113, 673–676. - PubMed
-
- Chen, C. Z., Li, L., Lodish, H. F. & Bartel, D. P. (2004) Science 303, 83–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

