Calcium signaling in mitral cell dendrites of olfactory bulbs of neonatal rats and mice during olfactory nerve Stimulation and beta-adrenoceptor activation
- PMID: 15286182
- PMCID: PMC498321
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.75204
Calcium signaling in mitral cell dendrites of olfactory bulbs of neonatal rats and mice during olfactory nerve Stimulation and beta-adrenoceptor activation
Abstract
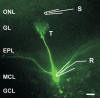
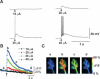
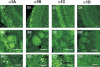
Synapses formed by the olfactory nerve (ON) provide the source of excitatory synaptic input onto mitral cells (MC) in the olfactory bulb. These synapses, which relay odor-specific inputs, are confined to the distally tufted single primary dendrites of MCs, the first stage of central olfactory processing. beta-adrenergic modulation of electrical and chemical signaling at these synapses may be involved in early odor preference learning. To investigate this possibility, we combined electrophysiological recordings with calcium imaging in olfactory bulb slices prepared from neonatal rats and mice. Activation of ON-MC synapses induced postsynaptic potentials, which were associated with large postsynaptic calcium transients. Neither electrical nor calcium responses were affected by beta-adrenergic agonists or antagonist. Immunocytochemical analysis of MCs and their tufted dendrites revealed clear immunoreactivity with antibodies against alpha1A (Cav2.1, P/Q-type) and alpha1B (Cav2.2, N-type), but not against alpha1C (Cav1.2, L-type) or alpha1D (Cav1.3, L-type) calcium channel subunits. Moreover, nimodipine, a blocker of L-type calcium channels, had no effect on either electrical or calcium signaling at ON-MC synapses. In contrast to previous evidence, we concluded that in neonatal rats and mice (P5-P8), mitral cells do not express significant amounts of L-type calcium channels, the calcium channel type that is often targeted by beta-adrenergic modulation. The absence of beta-adrenergic modulation on either electrical or calcium signaling at ON-MC synapses of neonatal rats and mice excludes the involvement of this mechanism in early odor preference learning.
Figures
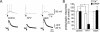
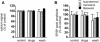
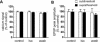

Similar articles
-
Olfactory nerve stimulation-induced calcium signaling in the mitral cell distal dendritic tuft.J Neurophysiol. 2006 Apr;95(4):2417-26. doi: 10.1152/jn.00964.2005. Epub 2005 Nov 30. J Neurophysiol. 2006. PMID: 16319202
-
Intraglomerular inhibition: signaling mechanisms of an olfactory microcircuit.Nat Neurosci. 2005 Mar;8(3):354-64. doi: 10.1038/nn1403. Epub 2005 Feb 6. Nat Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15696160
-
Altered synaptic transmission at olfactory and vomeronasal nerve terminals in mice lacking N-type calcium channel Cav2.2.Eur J Neurosci. 2014 Nov;40(10):3422-35. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12713. Epub 2014 Sep 5. Eur J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25195871
-
Electrical signaling in the olfactory bulb.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003 Aug;13(4):476-81. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(03)00092-8. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003. PMID: 12965296 Review.
-
Neuropharmacology of the olfactory bulb.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2008 Nov;1(3):181-90. doi: 10.2174/1874467210801030181. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 20021432 Review.
Cited by
-
Dendritic branching of olfactory bulb mitral and tufted cells: regulation by TrkB.PLoS One. 2009 Aug 25;4(8):e6729. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006729. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19707543 Free PMC article.
-
Early life trauma and attachment: immediate and enduring effects on neurobehavioral and stress axis development.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014 Mar 21;5:33. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00033. eCollection 2014. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014. PMID: 24711804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
α(1A)-Adrenergic regulation of inhibition in the olfactory bulb.J Physiol. 2013 Apr 1;591(7):1631-43. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.248591. Epub 2012 Dec 24. J Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23266935 Free PMC article.
-
A temporal-specific and transient cAMP increase characterizes odorant classical conditioning.Learn Mem. 2007 Mar 2;14(3):126-33. doi: 10.1101/lm.496007. Print 2007 Mar. Learn Mem. 2007. PMID: 17337703 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobiology of infant attachment.Dev Psychobiol. 2005 Nov;47(3):230-42. doi: 10.1002/dev.20093. Dev Psychobiol. 2005. PMID: 16252291 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Coopersmith, R. and Leon, M. 1995. Olfactory bulb glycogen metabolism: Noradrenergic modulation in the young rat. Brain Res. 647: 230-237. - PubMed
-
- Davila, N.G., Blakemore, L.J., and Trombley, P.Q. 2003. Dopamine modulates synaptic transmission between rat olfactory bulb neurons in culture. J. Neurophysiol. 90: 395-404. - PubMed
-
- Day, H.E., Campeau, S., Watson Jr., S.J., and Akil, H. 1997. Distribution of α 1a-, α 1b- and α 1d-adrenergic receptor mRNA in the rat brain and spinal cord. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 13: 115-139. - PubMed
-
- Friedman, D. and Strowbridge, B.W. 2000. Functional role of NMDA autoreceptors in olfactory mitral cells. J. Neurophysiol. 84: 39-50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
