Expanded B cell population blocks regulatory T cells and exacerbates ileitis in a murine model of Crohn disease
- PMID: 15286805
- PMCID: PMC484978
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI20855
Expanded B cell population blocks regulatory T cells and exacerbates ileitis in a murine model of Crohn disease
Abstract
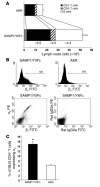
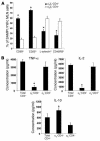
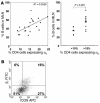
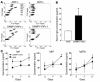
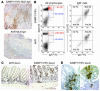
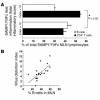
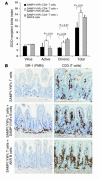
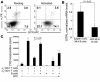
SAMP1/YitFc mice develop discontinuous, transmural inflammatory lesions in the terminal ileum, similar to what is found in human Crohn disease. Compared with the mesenteric lymph nodes (MLNs) of AKR control mice, SAMP1/YitFc MLNs contain a 4.3-fold expansion in total B cell number and a 2.5-fold increased percentage of CD4(+) T cells expressing the alpha(E)beta(7) integrin. Although alpha(E)beta(7)(+)CD4(+) T cells possess a regulatory phenotype (CD25(+), L-selectin(lo), and CD45RB(lo)), express IL-10, and suppress effector T cell proliferation in vitro, they cannot prevent ileitis development in SCID mice adoptively transferred with effector CD4(+) T cells, although the CD4(+)CD25(+) subset, which overlaps with the alpha(E)beta(7)(+)CD4(+) subset, prevents colitis. The alpha(E)beta(7)(+)CD4(+) T cells express high levels of ICOS, a costimulatory molecule that augments B cell function, suggesting their involvement in the increase in B cells, IgA(+) cells, and soluble IgA found within the MLNs and ileum of SAMP1/YitFc mice. MLN B cell numbers correlate with ileitis severity in SAMP1/YitFc mice, and cotransfer of SAMP1/YitFc MLN B cells along with CD4(+) T cells increases ileitis severity in SCID mice compared with transfer of CD4(+) T cells alone. SAMP1/YitFc B cells prevent alpha(E)beta(7)(+)CD4(+) T cells from suppressing effector T cell proliferation. We conclude that SAMP1/YitFc MLN B cells contribute to the development of SAMP1/YitFc ileitis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Beta7 integrin deficiency suppresses B cell homing and attenuates chronic ileitis in SAMP1/YitFc mice.J Immunol. 2010 Nov 1;185(9):5561-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903938. Epub 2010 Oct 6. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20926792 Free PMC article.
-
Proinflammatory effects of TH2 cytokines in a murine model of chronic small intestinal inflammation.Gastroenterology. 2005 Mar;128(3):654-66. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2004.11.053. Gastroenterology. 2005. PMID: 15765401
-
Emergence of perianal fistulizing disease in the SAMP1/YitFc mouse, a spontaneous model of chronic ileitis.Gastroenterology. 2003 Apr;124(4):972-82. doi: 10.1053/gast.2003.50148. Gastroenterology. 2003. PMID: 12671894
-
SAMP1/YitFc mouse strain: a spontaneous model of Crohn's disease-like ileitis.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011 Dec;17(12):2566-84. doi: 10.1002/ibd.21638. Epub 2011 May 6. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011. PMID: 21557393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenesis of gastritis in ileitis-prone SAMP1/Yit mice.Keio J Med. 2011;60(2):65-8. doi: 10.2302/kjm.60.65. Keio J Med. 2011. PMID: 21720202 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammatory bowel disease, past, present and future: lessons from animal models.J Gastroenterol. 2008;43(1):1-17. doi: 10.1007/s00535-007-2111-3. Epub 2008 Feb 24. J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18297430 Review.
-
Inflammatory bowel disease.N Engl J Med. 2009 Nov 19;361(21):2066-78. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0804647. N Engl J Med. 2009. PMID: 19923578 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
B cells and immunological tolerance.J Invest Dermatol. 2009 Feb;129(2):278-88. doi: 10.1038/jid.2008.240. J Invest Dermatol. 2009. PMID: 19148217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B cell-T cell interplay in immune regulation: A focus on follicular regulatory T and regulatory B cell functions.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 23;10:991840. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.991840. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36211467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BAFF promotes regulatory T-cell apoptosis and blocks cytokine production by activating B cells in primary biliary cirrhosis.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2013 May;46(5):433-9. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20132665. Epub 2013 May 10. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2013. PMID: 23681290 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elson CO. Genes, microbes, and T cells--new therapeutic targets in Crohn’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002;346:614–616. - PubMed
-
- Bouma G, Strober W. The immunological and genetic basis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003;3:521–533. - PubMed
-
- Dieckgraefe BK, Korzenik JR. Treatment of active Crohn’s disease with recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Lancet. 2002;360:1478–1480. - PubMed
-
- Dalwadi H, et al. B cell developmental requirement for the G alpha i2 gene. J. Immunol. 2003;170:1707–1715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

