Recruitment of the ArgR/Mcm1p repressor is stimulated by the activator Gcn4p: a self-checking activation mechanism
- PMID: 15289616
- PMCID: PMC511042
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0404652101
Recruitment of the ArgR/Mcm1p repressor is stimulated by the activator Gcn4p: a self-checking activation mechanism
Abstract
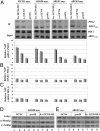
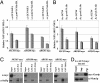
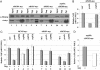
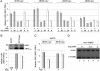
Transcription of the arginine biosynthetic gene ARG1 is repressed by the ArgR/Mcm1p complex in arginine-replete cells and activated by Gcn4p, a transcription factor induced by starvation for any amino acid. We show that all four subunits of the arginine repressor are recruited to ARG1 by Gcn4p in cells replete with arginine but starved for isoleucine/valine. None of these proteins is recruited to the Gcn4p target genes ARG4 and SNZ1, which are not regulated by ArgR/Mcm1p. Mcm1p and Arg80p were found in a soluble complex lacking Arg81p and Arg82p, and both Mcm1p and Arg80p were efficiently recruited to ARG1 in wild-type cells in the presence or absence of exogenous arginine, and also in arg81Delta cells. By contrast, the recruitment of Arg81p and Arg82p was stimulated by exogenous arginine. These findings suggest that Gcn4p constitutively recruits an Mcm1p/Arg80p heterodimer and that efficient assembly of a functional repressor also containing Arg81p and Arg82p occurs only in arginine excess. By recruiting an arginine-regulated repressor, Gcn4p can precisely modulate its activation function at ARG1 according to the availability of arginine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activator Gcn4p and Cyc8p/Tup1p are interdependent for promoter occupancy at ARG1 in vivo.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Dec;25(24):11171-83. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.24.11171-11183.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16314536 Free PMC article.
-
Mcm1p binding sites in the ARG1 promoter positively regulate ARG1 transcription and S. cerevisiae growth in the absence of arginine and Gcn4p.Amino Acids. 2011 Feb;40(2):623-31. doi: 10.1007/s00726-010-0687-z. Epub 2010 Jul 13. Amino Acids. 2011. PMID: 20625780
-
Further definition of the sequence and position requirements of the arginine control element that mediates repression and induction by arginine in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Yeast. 1995 Nov;11(14):1367-80. doi: 10.1002/yea.320111405. Yeast. 1995. PMID: 8585320
-
Controlling transcription by destruction: the regulation of yeast Gcn4p stability.Curr Genet. 2003 Oct;44(1):8-18. doi: 10.1007/s00294-003-0422-3. Epub 2003 Jul 9. Curr Genet. 2003. PMID: 14508604 Review.
-
Gcn4p, a master regulator of gene expression, is controlled at multiple levels by diverse signals of starvation and stress.Eukaryot Cell. 2002 Feb;1(1):22-32. doi: 10.1128/EC.01.1.22-32.2002. Eukaryot Cell. 2002. PMID: 12455968 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Activation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae HIS3 results in Gcn4p-dependent, SWI/SNF-dependent mobilization of nucleosomes over the entire gene.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Nov;26(22):8607-22. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00678-06. Epub 2006 Sep 18. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16982689 Free PMC article.
-
Inositol phosphate multikinase dependent transcriptional control.Adv Biol Regul. 2017 May;64:9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2017.03.001. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Adv Biol Regul. 2017. PMID: 28342784 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide cooperation by HAT Gcn5, remodeler SWI/SNF, and chaperone Ydj1 in promoter nucleosome eviction and transcriptional activation.Genome Res. 2016 Feb;26(2):211-25. doi: 10.1101/gr.196337.115. Epub 2015 Nov 24. Genome Res. 2016. PMID: 26602697 Free PMC article.
-
GRIP1-associated SET-domain methyltransferase in glucocorticoid receptor target gene expression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Dec 23;105(51):20185-90. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810863105. Epub 2008 Dec 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 19074285 Free PMC article.
-
Roles for inositol polyphosphate kinases in the regulation of nuclear processes and developmental biology.Adv Enzyme Regul. 2007;47:10-25. doi: 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2006.12.019. Epub 2007 Jan 5. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2007. PMID: 17467778 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Hinnebusch, A. G. (1992) in The Molecular and Cellular Biology of the Yeast Saccharomyces: Gene Expression, eds. Broach, J. R., Jones, E. W. & Pringle, J. R. (Cold Spring Harbor Lab. Press, Plainview, NY), pp. 319–414.
-
- Messenguy, F. & Dubois, E. (2003) Gene 316, 1–21. - PubMed
-
- Crabeel, M., de Rijcke, M., Seneca, S., Heimberg, H., Pfeiffer, I. & Matisova, A. (1995) Yeast 11, 1367–1380. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

