ATM and ataxia telangiectasia
- PMID: 15289825
- PMCID: PMC1299121
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400210
ATM and ataxia telangiectasia
Abstract
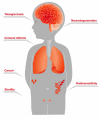
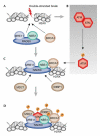
Ataxia telangiectasia (AT) has long intrigued the biomedical research community owing to the spectrum of defects that are characteristic of the disease, including neurodegeneration, immune dysfunction, radiosensitivity and cancer predisposition. Following the identification of mutations in ATM (ataxia telangiectasia, mutated) as the underlying cause of the disease, biochemical analysis of this protein kinase has shown that it is a crucial nexus for the cellular response to DNA double-stranded breaks. Many ATM kinase substrates are important players in the cellular responses that prevent cancer. Accordingly, AT is a disease that results from defects in the response to specific types of DNA damage. Thus, although it is a rare neurodegenerative disease, understanding the biology of AT will lead to a greater understanding of the fundamental processes that underpin cancer and neurodegeneration.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ATM and the molecular pathogenesis of ataxia telangiectasia.Annu Rev Pathol. 2012;7:303-21. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-011811-132509. Epub 2011 Oct 24. Annu Rev Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22035194 Review.
-
Many faces of ATM: eighth international workshop on ataxia-telangiectasia.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999 Oct 29;1424(2-3):R45-55. doi: 10.1016/s0304-419x(99)00023-2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999. PMID: 10528155 No abstract available.
-
Ataxia-telangiectasia and related diseases.Neuromolecular Med. 2006;8(4):495-511. doi: 10.1385/NMM:8:4:495. Neuromolecular Med. 2006. PMID: 17028372 Review.
-
Oxidative stress in ataxia telangiectasia.Redox Rep. 2003;8(1):23-9. doi: 10.1179/135100003125001206. Redox Rep. 2003. PMID: 12631440 Review.
-
ATM: the protein encoded by the gene mutated in the radiosensitive syndrome ataxia-telangiectasia.Int J Radiat Biol. 1999 Oct;75(10):1201-14. doi: 10.1080/095530099139359. Int J Radiat Biol. 1999. PMID: 10549596 Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear GIT2 is an ATM substrate and promotes DNA repair.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Apr;35(7):1081-96. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01432-14. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25605334 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytes restore connectivity and synchronization in dysfunctional cerebellar networks.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Jul 31;115(31):8025-8030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1718582115. Epub 2018 Jul 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30012604 Free PMC article.
-
Post-mitotic role of the cell cycle machinery.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013 Dec;25(6):711-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2013.08.001. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24055434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATM is a key driver of NF-κB-dependent DNA-damage-induced senescence, stem cell dysfunction and aging.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Mar 22;12(6):4688-4710. doi: 10.18632/aging.102863. Epub 2020 Mar 22. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32201398 Free PMC article.
-
Ataxia telangiectasia derived iPS cells show preserved x-ray sensitivity and decreased chromosomal instability.Sci Rep. 2014 Jun 27;4:5421. doi: 10.1038/srep05421. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24970375 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abner CW, McKinnon PJ (2004) The DNA doublestrand break response in the nervous system. DNA Repair (Amst) (in press) - PubMed
-
- Angele S et al. (2003) ATM haplotypes and cellular response to DNA damage: association with breast cancer risk and clinical radiosensitivity. Cancer Res 63: 8717–8725 - PubMed
-
- Baker SJ, McKinnon PJ (2004) Tumoursuppressor function in the nervous system. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 184–196 - PubMed
-
- Bakkenist CJ, Kastan MB (2003) DNA damage activates ATM through intermolecular autophosphorylation and dimer dissociation. Nature 421: 499–506 - PubMed
-
- Barlow C, Liyanage M, Moens PB, Deng CX, Ried T, Wynshaw-Boris A (1997) Partial rescue of the prophase I defects of Atm-deficient mice by p53 and p21 null alleles. Nat Genet 17: 462–466 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

