Integrated evaluation of DNA sequence variants of unknown clinical significance: application to BRCA1 and BRCA2
- PMID: 15290653
- PMCID: PMC1182042
- DOI: 10.1086/424388
Integrated evaluation of DNA sequence variants of unknown clinical significance: application to BRCA1 and BRCA2
Abstract
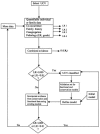
Many sequence variants in predisposition genes are of uncertain clinical significance, and classification of these variants into high- or low-risk categories is an important problem in clinical genetics. Classification of such variants can be performed by direct epidemiological observations, including cosegregation with disease in families and degree of family history of the disease, or by indirect measures, including amino acid conservation, severity of amino acid change, and evidence from functional assays. In this study, we have developed an approach to the synthesis of such evidence in a multifactorial likelihood-ratio model. We applied this model to the analysis of three unclassified variants in BRCA1 and three in BRCA2. The evidence strongly suggests that two variants (C1787S in BRCA1 and D2723H in BRCA2) are deleterious, three (R841W in BRCA1 and Y42C and P655R in BRCA2) are neutral, and one (R1699Q in BRCA1) remains of uncertain significance. These results provide a demonstration of the utility of the model.
Figures
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Berkeley Drosophila Genome Project, http://www.fruitfly.org/seq_tools/splice.html (for splice-site analysis)
-
- Breast Cancer Information Core (BIC) database, http://research.nhgri.nih.gov/bic/
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for BRCA1 and BRCA2)
References
-
- Antoniou A, Pharoah PD, Narod S, Risch HA, Eyfjord JE, Hopper JL, Loman N, et al (2003) Average risks of breast and ovarian cancer associated with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations detected in case series unselected for family history: a combined analysis of 22 studies. Am J Hum Genet 72:1117–1130 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous