The LuxR homolog ExpR, in combination with the Sin quorum sensing system, plays a central role in Sinorhizobium meliloti gene expression
- PMID: 15292148
- PMCID: PMC490858
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.16.5460-5472.2004
The LuxR homolog ExpR, in combination with the Sin quorum sensing system, plays a central role in Sinorhizobium meliloti gene expression
Abstract
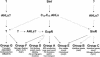
Quorum sensing, a population density-dependent mechanism for bacterial communication and gene regulation, plays a crucial role in the symbiosis between alfalfa and its symbiont Sinorhizobium meliloti. The Sin system, one of three quorum sensing systems present in S. meliloti, controls the production of the symbiotically active exopolysaccharide EPS II. Based on DNA microarray data, the Sin system also seems to regulate a multitude of S. meliloti genes, including genes that participate in low-molecular-weight succinoglycan production, motility, and chemotaxis, as well as other cellular processes. Most of the regulation by the Sin system is dependent on the presence of the ExpR regulator, a LuxR homolog. Gene expression profiling data indicate that ExpR participates in additional cellular processes that include nitrogen fixation, metabolism, and metal transport. Based on our microarray analysis we propose a model for the regulation of gene expression by the Sin/ExpR quorum sensing system and another possible quorum sensing system(s) in S. meliloti.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[A LuxR family regulator, ExpR regulates the expression of motC operon from Sinorhizobium meliloti].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2006 Jun;46(3):474-7. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2006. PMID: 16933625 Chinese.
-
Regulation of motility by the ExpR/Sin quorum-sensing system in Sinorhizobium meliloti.J Bacteriol. 2008 Feb;190(3):861-71. doi: 10.1128/JB.01310-07. Epub 2007 Nov 16. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18024512 Free PMC article.
-
A LuxR homolog controls production of symbiotically active extracellular polysaccharide II by Sinorhizobium meliloti.J Bacteriol. 2002 Sep;184(18):5067-76. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.18.5067-5076.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12193623 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of succinoglycan and galactoglucan biosynthesis in Sinorhizobium meliloti.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002 May;4(3):187-90. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002. PMID: 11931545 Review.
-
Genetic regulation of nitrogen fixation in Rhizobium meliloti.Microbiologia. 1994 Dec;10(4):371-84. Microbiologia. 1994. PMID: 7772292 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of Quorum Sensing as an Adaptation to Nodule Cell Infection during Experimental Evolution of Legume Symbionts.mBio. 2020 Jan 28;11(1):e03129-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03129-19. mBio. 2020. PMID: 31992622 Free PMC article.
-
A perspective on inter-kingdom signaling in plant-beneficial microbe interactions.Plant Mol Biol. 2016 Apr;90(6):537-48. doi: 10.1007/s11103-016-0433-3. Epub 2016 Jan 20. Plant Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26792782 Review.
-
Botrytis cinerea manipulates the antagonistic effects between immune pathways to promote disease development in tomato.Plant Cell. 2011 Jun;23(6):2405-21. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.083394. Epub 2011 Jun 10. Plant Cell. 2011. PMID: 21665999 Free PMC article.
-
Novel mixed-linkage β-glucan activated by c-di-GMP in Sinorhizobium meliloti.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Feb 17;112(7):E757-65. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1421748112. Epub 2015 Feb 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25650430 Free PMC article.
-
ExpR is not required for swarming but promotes sliding in Sinorhizobium meliloti.J Bacteriol. 2012 Apr;194(8):2027-35. doi: 10.1128/JB.06524-11. Epub 2012 Feb 10. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22328673 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ang, S., Y. T. Horng, J. C. Shu, P. C. Soo, J. H. Liu, W. C. Yi, L. H. C., K. T. Luh, S. W. Ho, and S. Swift. 2001. The role of RsmA in the regulation of swarming motility in Serratia marcescens. J. Biomed. Sci. 8:160-169. - PubMed
-
- Becker, A., H. Bergès, E. Krol, C. Bruand, S. Rüberg, D. Capela, E. Lauber, E. Meilhoc, A. Ampe, F. J. de Bruijn, J. Fourment, A. Francez-Charlot, D. Kahn, H. Küster, C. Liebe, A. Pühler, S. Weidner, and J. Batut. 2004. Global changes in gene expression in Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 under microoxic and symbiotic conditions. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 17:292-303. - PubMed
-
- Becker, A., K. Niehaus, and A. Pühler. 1995. Low-molecular-weight succinoglycan is predominantly produced by Rhizobium meliloti strains carrying a mutated ExoP protein characterized by a periplasmic N-terminal domain and a missing C-terminal domain. Mol. Microbiol. 16:191-203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

