Glutamate released from glial cells synchronizes neuronal activity in the hippocampus
- PMID: 15295027
- PMCID: PMC6729611
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0473-04.2004
Glutamate released from glial cells synchronizes neuronal activity in the hippocampus
Erratum in
- J Neurosci. 2004 Aug 25;24(34):2p following 7575
Abstract
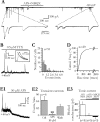
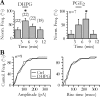
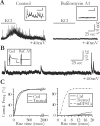
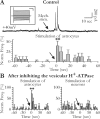
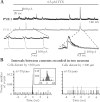
Glial cells of the nervous system directly influence neuronal and synaptic activities by releasing transmitters. However, the physiological consequences of this glial transmitter release on brain information processing remain poorly understood. We demonstrate here in hippocampal slices of 2- to 5-week-old rats that glutamate released from glial cells generates slow transient currents (STCs) mediated by the activation of NMDA receptors in pyramidal cells. STCs persist in the absence of neuronal and synaptic activity, indicating a nonsynaptic origin of the source of glutamate. Indeed, STCs occur spontaneously but can also be induced by pharmacological tools known to activate astrocytes and by the selective mechanical stimulation of single nearby glial cells. Bath application of the inhibitor of the glutamate uptake dl-threo-beta-benzyloxyaspartate increases both the frequency of STCs and the amplitude of a tonic conductance mediated by NMDA receptors and probably also originated from glial glutamate release. By using dual recordings, we observed synchronized STCs in pyramidal cells having their soma distant by <100 microm. The degree of precision (<100 msec) of this synchronization rules out the involvement of calcium waves spreading through the glial network. It also indicates that single glial cells release glutamate onto adjacent neuronal processes, thereby controlling simultaneously the excitability of several neighboring pyramidal cells. In conclusion, our results show that the glial glutamate release occurs spontaneously and synchronizes the neuronal activity in the hippocampus.
Figures

References
-
- Araque A, Parpura V, Sanzgiri RP, Haydon PG (1998a) Glutamate-dependent astrocyte modulation of synaptic transmission between cultured hippocampal neurons. Eur J Neurosci 10: 2129-2142. - PubMed
-
- Araque A, Parpura V, Sanzgiri RP, Haydon PG (1999) Tripartite synapses: glia, the unacknowledged partner. Trends Neurosci 22: 208-215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
