Pathways towards and away from Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 15295589
- PMCID: PMC3091392
- DOI: 10.1038/nature02621
Pathways towards and away from Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
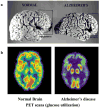
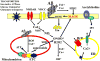
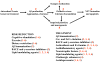
Slowly but surely, Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients lose their memory and their cognitive abilities, and even their personalities may change dramatically. These changes are due to the progressive dysfunction and death of nerve cells that are responsible for the storage and processing of information. Although drugs can temporarily improve memory, at present there are no treatments that can stop or reverse the inexorable neurodegenerative process. But rapid progress towards understanding the cellular and molecular alterations that are responsible for the neuron's demise may soon help in developing effective preventative and therapeutic strategies.
Figures
References
-
- Dickson DW. Neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: a perspective from longitudinal clinicopathological studies. Neurobiol Aging. 1997;18:S21–26. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Evolution of neuronal changes in the course of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1998;53:127–140. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe DJ, Schenk D. Alzheimer’s disease: molecular understanding predicts amyloid-based therapeutics. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2003;43:545–584. - PubMed
-
- Hardy J. Amyloid, the presenilins and Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Neurosci. 1997;20:154–159. - PubMed
-
- Sherrington R, et al. Cloning of a gene bearing missense mutations in early-onset familial Alzheimer’s disease. Nature. 1995;375:754–760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

