Clinical evaluation of the digene hybrid capture II test and the COBAS AMPLICOR monitor test for determination of hepatitis B virus DNA levels
- PMID: 15297491
- PMCID: PMC497578
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.8.3513-3517.2004
Clinical evaluation of the digene hybrid capture II test and the COBAS AMPLICOR monitor test for determination of hepatitis B virus DNA levels
Abstract
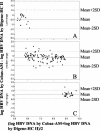
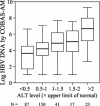
The measurement of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA is important for the assessment of liver disease and treatment efficacy. Most commercially available assays for the determination of HBV DNA levels have limited linear ranges. This study was performed to evaluate the clinical performance of the Digene Hybrid Capture II (Digene HC II assay) and the COBAS AMPLICOR Monitor test (COBAS-AM assay), with special emphasis on anti-HBV e antigen (HBeAg)-positive patients with low HBV DNA levels. A total of 425 Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B were recruited. A total of 107 patients were HBeAg positive, and 318 patients were HBeAg negative. The Digene HC II assay and the COBAS-AM assay had similar intra-assay and interassay variabilities. A total of 264 patients (62.1%) had HBV DNA levels undetectable by the Digene HC II assay, and 47 patients (11.1%) had HBV DNA levels undetectable by the COBAS-AM assay (P < 0.001). For the 161 patients with HBV DNA levels detectable by the Digene HC II assay, the HBV DNA levels obtained by the Digene HC II assay and by the COBAS-AM assay showed an excellent correlation (r = 0.95; P < 0.001). The linear ranges of the Digene HC II assay and the COBAS-AM assay marginally overlapped. Before HBV DNA levels could be determined by the COBAS-AM assay, predilution had to be performed for 158 of 161 patients (98.1%) with HBV DNA levels detectable by the Digene HC II assay and for 10 of 264 patients (3.8%) with HBV DNA levels undetectable by the Digene HC II assay. The cost for assaying each serum sample by using different strategies was calculated. The COBAS-AM assay was more sensitive than the Digene HC II assay and more suitable for monitoring low levels of HBV viremia.
Figures

References
-
- Bland, J. M., and D. G. Altman. 1986. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1:307-310. - PubMed
-
- Niesters, H. G., M. Krajden, L. Cork, M. de Medina, M. Hill, E. Fries, and A. D. Osterhaus. 2000. A multicenter study evaluation of the Digene hybrid capture II signal amplification technique for detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in serum samples and testing of EUROHEP standards. J. Clin. Microbiol. 38:2150-2155. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pawlotsky, J. M. 2002. Molecular diagnosis of viral hepatitis. Gastroenterology 122:1554-1568. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

