Cryptococcus infection in tropical Australia
- PMID: 15297551
- PMCID: PMC497626
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.8.3865-3868.2004
Cryptococcus infection in tropical Australia
Abstract
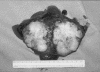
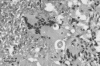
Eighteen cases of disease caused by the saprophytic fungi Cryptococcus neoformans and Cryptococcus bacillisporus are described from the Northern Territory of Australia. The majority of infections were with Cryptococcus bacillisporus and in the rural Aboriginal population, often causing pulmonary mass lesions.
Figures
References
-
- Aberg, J. A., L. M. Mundy, and W. G. Powderly. 1999. Pulmonary cryptococcosis in patients without HIV infection. Chest 115:734-740. - PubMed
-
- Chen, S., T. Sorrell, G. Nimmo, B. Speed, B. Currie, D. Ellis, D. Marriott, T. Pfeiffer, D. Parr, K. Byth, et al. 2000. Epidemiology and host- and variety-dependent characteristics of infection due to Cryptococcus neoformans in Australia and New Zealand. Clin. Infect. Dis. 31:499-508. - PubMed
-
- Chen, S. C. A., B. Currie, H. M. Campbell, D. A. Fisher, T. J. Pfeiffer, D. H. Ellis, and T. C. Sorrell. 1997. Cryptococcus neoformans var. gattii infection in Northern Australia: existence of environmental source other than known host eucalypts. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 91:547-550. - PubMed
-
- Diamond, R. 2000. Cryptococcus neoformans, p. 2707. In G. L. Mandell, J. E. Bennett, and R. Dolin (ed.), Principles and practice of infectious diseases, 5th ed. Churchill Livingstone, New York, N.Y.
-
- Fisher, D., J. Burrow, D. Lo, and B. Currie. 1993. Cryptococcosis neoformans in tropical northern Australia: predominantly variant gattii with good outcomes. Aust. N. Z. J. Med. 23:678-682. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

