Structure of human annexin a6 at the air-water interface and in a membrane-bound state
- PMID: 15298924
- PMCID: PMC1304460
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.103.038240
Structure of human annexin a6 at the air-water interface and in a membrane-bound state
Abstract
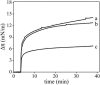
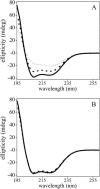
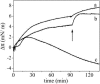
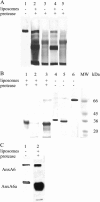
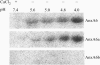
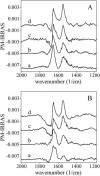
We postulate the existence of a pH-sensitive domain in annexin A6 (AnxA6), on the basis of our observation of pH-dependent conformational and orientation changes of this protein and its N- (AnxA6a) and C-terminal (AnxA6b) halves in the presence of lipids. Brewster angle microscopy shows that AnxA6, AnxA6a, and AnxA6b in the absence of lipids accumulate at the air-water interface and form a stable, homogeneous layer at pH below 6.0. Under these conditions polarization modulation IR absorption spectroscopy reveals significant conformational changes of AnxA6a whereas AnxA6b preserves its alpha-helical structure. The orientation of protein alpha-helices is parallel with respect to the interface. In the presence of lipids, polarization modulation IR reflection absorption spectroscopy experiments suggest that AnxA6a incorporates into the lipid/air interface, whereas AnxA6b is adsorbed under the lipid monolayer. In this case AnxA6a regains its alpha-helical structures. At a higher pressure of the lipid monolayer the average orientation of the alpha-helices of AnxA6a changes from flat to tilted by 45 degrees with respect to normal to the membrane interface. For AnxA6b no such changes are detected, even at a high pressure of the lipid monolayer-suggesting that the putative pH-sensitive domain of AnxA6 is localized in the N-terminal half of the protein.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A putative consensus sequence for the nucleotide-binding site of annexin A6.Biochemistry. 2003 Aug 5;42(30):9137-46. doi: 10.1021/bi034359m. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12885247
-
Influence of the 524-VAAEIL-529 sequence of annexins A6 in their interfacial behavior and interaction with lipid monolayers.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2013 Aug 1;403:99-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2013.04.029. Epub 2013 Apr 29. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2013. PMID: 23683957
-
Interaction of annexin A6 with cholesterol rich membranes is pH-dependent and mediated by the sterol OH.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2010 Jun 15;346(2):436-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2010.03.015. Epub 2010 Mar 12. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2010. PMID: 20363475
-
Lipid monolayers: why use half a membrane to characterize protein-membrane interactions?Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1999 Aug;9(4):438-43. doi: 10.1016/S0959-440X(99)80061-X. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1999. PMID: 10449364 Review.
-
Infrared reflection-absorption spectroscopy: principles and applications to lipid-protein interaction in Langmuir films.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Apr;1798(4):788-800. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2009.11.024. Epub 2010 Jan 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20004639 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structure-function relationship in annexin A13, the founder member of the vertebrate family of annexins.Biochem J. 2005 Aug 1;389(Pt 3):899-911. doi: 10.1042/BJ20041918. Biochem J. 2005. PMID: 15813707 Free PMC article.
-
Annexins as organizers of cholesterol- and sphingomyelin-enriched membrane microdomains in Niemann-Pick type C disease.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Jun;69(11):1773-85. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0894-0. Epub 2011 Dec 13. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22159585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human islet amyloid polypeptide at the air-aqueous interface: a Langmuir monolayer approach.J R Soc Interface. 2012 Nov 7;9(76):3118-28. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2012.0368. Epub 2012 Jul 11. J R Soc Interface. 2012. PMID: 22787008 Free PMC article.
-
Annexin-phospholipid interactions. Functional implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Jan 28;14(2):2652-83. doi: 10.3390/ijms14022652. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23358253 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial creatine kinase binding to phospholipid monolayers induces cardiolipin segregation.Biophys J. 2009 Mar 18;96(6):2428-38. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2008.12.3911. Biophys J. 2009. PMID: 19289067 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avila-Sakar, A. J., C. E. Creutz, and R. H. Kretsinger. 1998. Crystal structure of bovine annexin VI in a calcium-bound state. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1387:103–116. - PubMed
-
- Avila-Sakar, A. J., R. H. Kretsinger, and C. E. Creutz. 2000. Membrane-bound 3D structures reveal the intrinsic flexibility of annexin VI. J. Struct. Biol. 130:54–62. - PubMed
-
- Bandorowicz-Pikula, J., A. Kirilenko, R. van Deursen, M. Golczak, M. Kuhnel, J. M. Lancelin, S. Pikula, and R. Buchet. 2003. A putative consensus sequence for the nucleotide-binding site of annexin A6. Biochemistry. 42:9137–9146. - PubMed
-
- Benz, J., A. Bergner, A. Hofmann, P. Demange, P. Gottig, S. Liemann, R. Huber, and D. Voges. 1996. The structure of recombinant human annexin VI in crystals and membrane-bound. J. Mol. Biol. 260:638–643. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

