Utility of different gene enrichment approaches toward identifying and sequencing the maize gene space
- PMID: 15299128
- PMCID: PMC523364
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.104.043323
Utility of different gene enrichment approaches toward identifying and sequencing the maize gene space
Abstract
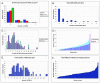
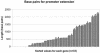
Maize (Zea mays) possesses a large, highly repetitive genome, and subsequently a number of reduced-representation sequencing approaches have been used to try and enrich for gene space while eluding difficulties associated with repetitive DNA. This article documents the ability of publicly available maize expressed sequence tag and Genome Survey Sequences (GSSs; many of which were isolated through the use of reduced representation techniques) to recognize and provide coverage of 78 maize full-length cDNAs (FLCs). All 78 FLCs in the dataset were identified by at least three GSSs, indicating that the majority of maize genes have been identified by at least one currently available GSS. Both methyl-filtration and high-Cot enrichment methods provided a 7- to 8-fold increase in gene discovery rates as compared to random sequencing. The available maize GSSs aligned to 75% of the FLC nucleotides used to perform searches, while the expressed sequence tag sequences aligned to 73% of the nucleotides. Our data suggest that at least approximately 95% of maize genes have been tagged by at least one GSS. While the GSSs are very effective for gene identification, relatively few (18%) of the FLCs are completely represented by GSSs. Analysis of the overlap of coverage and bias due to position within a gene suggest that RescueMu, methyl-filtration, and high-Cot methods are at least partially nonredundant.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Enrichment of gene-coding sequences in maize by genome filtration.Science. 2003 Dec 19;302(5653):2118-20. doi: 10.1126/science.1090047. Science. 2003. PMID: 14684821
-
Reduced representation sequencing: a success in maize and a promise for other plant genomes.Bioessays. 2005 Aug;27(8):839-48. doi: 10.1002/bies.20262. Bioessays. 2005. PMID: 16015589
-
High-Cot sequence analysis of the maize genome.Plant J. 2003 Apr;34(2):249-55. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2003.01716.x. Plant J. 2003. PMID: 12694599
-
Progress in maize gene discovery: a project update.Funct Integr Genomics. 2003 Mar;3(1-2):25-32. doi: 10.1007/s10142-002-0078-y. Epub 2002 Oct 1. Funct Integr Genomics. 2003. PMID: 12590340 Review.
-
The maize genome as a model for efficient sequence analysis of large plant genomes.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2006 Apr;9(2):149-56. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2006.01.015. Epub 2006 Feb 3. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2006. PMID: 16459129 Review.
Cited by
-
Towards decoding the conifer giga-genome.Plant Mol Biol. 2012 Dec;80(6):555-69. doi: 10.1007/s11103-012-9961-7. Epub 2012 Sep 9. Plant Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22960864 Review.
-
Gene enrichment in maize with hypomethylated partial restriction (HMPR) libraries.Genome Res. 2005 Oct;15(10):1441-6. doi: 10.1101/gr.3362105. Genome Res. 2005. PMID: 16204197 Free PMC article.
-
Extension of Lander-Waterman theory for sequencing filtered DNA libraries.BMC Bioinformatics. 2005 Oct 10;6:245. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-245. BMC Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 16216129 Free PMC article.
-
Uneven chromosome contraction and expansion in the maize genome.Genome Res. 2006 Oct;16(10):1241-51. doi: 10.1101/gr.5338906. Epub 2006 Aug 10. Genome Res. 2006. PMID: 16902087 Free PMC article.
-
The TIGR Maize Database.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jan 1;34(Database issue):D771-6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj072. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16381977 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408: 796–815 - PubMed
-
- Arumuganathan K, Earle ED (1991) Nuclear DNA content of some important plant species. Plant Mol Biol 42: 251–269
-
- Bennetzen JL (1996) The contributions of retroelements to plant genome organization, function and evolution. Trends Microbiol 4: 347–353 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

