Effect of interleukin-10 and platelet-derived growth factor on expressions of matrix metalloproteinases-2 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 in rat fibrotic liver and cultured hepatic stellate cells
- PMID: 15300910
- PMCID: PMC4572167
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i17.2574
Effect of interleukin-10 and platelet-derived growth factor on expressions of matrix metalloproteinases-2 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 in rat fibrotic liver and cultured hepatic stellate cells
Abstract
Aim: To examine the expressions of matrix metalloproteinases-2 (MMP-2) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP-1) in rat fibrotic liver and in normal rat hepatic stellate cells, and to investigate the changes in their expressions in response to treatment with interleukin-10 (IL-10) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF).
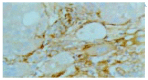
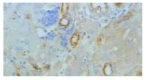
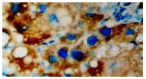
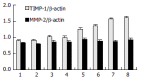
Methods: Rat models of CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis were established and the liver tissues were sampled from the rats with or without IL-10 treatment, and also from the control rats. The expressions of MMP-2 and TIMP-1 in liver tissues were detected by S-P immunohistochemistry, and their expression intensities were evaluated in different groups. Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) were isolated from normal rat and cultured in vitro prior to exposure to PDGF treatment or co-treatment with IL-10 and PDGF. MMP-2 and TIMP-1 levels were measured by semi-quantitative reverse transcriptional polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
Results: CCl4- induced rat hepatic fibrosis models were successfully established. The positive expressions of MMP-2 and TIMP-1 increased obviously with the development of hepatic fibrosis, especially in untreated model group (84.0% and 92.0%, P<0.01). The positive signals decreased significantly following IL-10 treatment (39.3% and 71.4%, P<0.01 and P<0.05) in a time-dependent manner. TIMP-1 mRNA in PDGF-treated group was significantly increased time-dependently in comparison with that of the control group, but PDGF did not obviously affect MMP-2 expression. No difference was noted in TIMP-1 and MMP-2 expressions in HSCs after IL-10 and PDGF treatment (P>0.05).
Conclusion: MMP-2 and TIMP-1 expressions increase in liver tissues with the development of fibrosis, which can be inhibited by exogenous IL-10 inhibitor. PDGF induces the up-regulation of TIMP-1 but not MMP-2 in the HSCs. IL-10 inhibits TIMP-1 and MMP-2 expressions in HSCs induced by PDGF.
Copyright 2004 The WJG Press ISSN
Figures


Similar articles
-
Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in hepatic stellate cells during rat hepatic fibrosis and its intervention by IL-10.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Mar 28;11(12):1753-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i12.1753. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 15793858 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of platelet-derived growth factor and interleukin-10 on Fas/Fas-ligand and Bcl-2/Bax mRNA expression in rat hepatic stellate cells in vitro.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Sep 15;10(18):2706-10. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i18.2706. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15309723 Free PMC article.
-
Naringin from Ganshuang granule inhibits inflammatory to relieve liver fibrosis through TGF-β-Smad signaling pathway.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 10;19(6):e0304185. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0304185. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38857261 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of Shaoqiduogan on MMP-13, TIMP-1 expression in liver and hepatic stellate cells of hepatic fibrosis rats].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2010 Jun;35(11):1447-51. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 20822018 Chinese.
-
Matrix metalloproteinases, the pros and cons, in liver fibrosis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006 Oct;21 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S88-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04586.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006. PMID: 16958682 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic effect of interleukin-10 on CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Mar 7;12(9):1386-91. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i9.1386. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16552806 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiology of chronic pancreatitis induced by dibutyltin dichloride joint ethanol in mice.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Mar 14;22(10):2960-70. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i10.2960. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26973392 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha ameliorates ethanol mediated liver fibrosis in mice.Lipids Health Dis. 2013 Feb 6;12:11. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-12-11. Lipids Health Dis. 2013. PMID: 23388073 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-10 and chronic liver disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Mar 21;12(11):1681-5. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i11.1681. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16586534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA interference targeting the platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta subunit ameliorates experimental hepatic fibrosis in rats.Liver Int. 2008 Dec;28(10):1446-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2008.01759.x. Epub 2008 May 3. Liver Int. 2008. PMID: 18466260 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bedossa P, Paradis V. Liver extracellular matrix in health and disease. J Pathol. 2003;200:504–515. - PubMed
-
- Rockey DC. The cell and molecular biology of hepatic fibrogenesis. Clinical and therapeutic implications. Clin Liver Dis. 2000;4:319–355. - PubMed
-
- Bataller R, Brenner DA. Hepatic stellate cells as a target for the treatment of liver fibrosis. Semin Liver Dis. 2001;21:437–451. - PubMed
-
- Safadi R, Friedman SL. Hepatic fibrosis--role of hepatic stellate cell activation. MedGenMed. 2002;4:27. - PubMed
-
- Reeves HL, Friedman SL. Activation of hepatic stellate cells--a key issue in liver fibrosis. Front Biosci. 2002;7:d808–d826. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

