Binding affinity of lactose permease is not altered by the H+ electrochemical gradient
- PMID: 15304639
- PMCID: PMC514448
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0404936101
Binding affinity of lactose permease is not altered by the H+ electrochemical gradient
Abstract
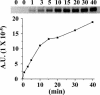
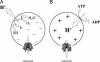
The x-ray structure of lactose permease of Escherichia coli (LacY) exhibits a single sugar-binding site at the apex of a hydrophilic cavity open to the cytoplasm, and it has been postulated that the binding site has alternating access to either side of the membrane during turnover. Here, the affinity of LacY for ligand in right-side-out or inside-out membrane vesicles is measured in the absence or presence of an H(+) electrochemical gradient (Deltamicro(H(+))) by utilizing ligand protection against alkylation. Right-side-out or inside-out membrane vesicles containing LacY with a single cysteine residue at position 148 exhibit K(D) values for lactose or beta-d-galactopyranosyl 1-thio-beta-d-galactopyranoside of approximately 1.0 mM or 40 microM, respectively, and no systematic change is observed in the presence of Deltamicro(H(+)) under conditions in which there is little or no accumulation of ligand. The results are consistent with a mechanism in which the major effect of Deltamicro(H(+)) on sugar accumulation is caused by an increased rate of deprotonation on the inner face of the membrane, leading to an increase in the rate of return of the unloaded symporter to the outer face of the membrane.
Figures


References
-
- Saier, M. H., Jr. (2000) Mol. Microbiol. 35, 699-710. - PubMed
-
- Kaback, H. R., Sahin-Tóth, M. & Weinglass, A. B. (2001) Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2, 610-620. - PubMed
-
- Schuldiner, S. & Kaback, H. R. (1977) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 472, 399-418. - PubMed
-
- Frillingos, S. & Kaback, H. R. (1996) Biochemistry 35, 3950-3956. - PubMed
-
- Lolkema, J. S., Carrasco, N. & Kaback, H. R. (1991) Biochemistry 30, 1284-1290. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

